江政洪 冯美英


[关键词] Pilon骨折;微创接骨板技术;踝关节Olreud-Molander功能评分;并发症
[中图分类号] R687.3 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)19-0089-03
Study on the clinical efficacy of MIPO in the treatment of Pilon fracture
JIANG Zhenghong1 FENG Meiying2
1.The Second Department of Bone Injury, Jingdezhen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangxi Province, Jingdezhen 333000, China; 2.The First Department of Surgery, Jingdezhen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Jiangxi Province, Jingdezhen 333000, China
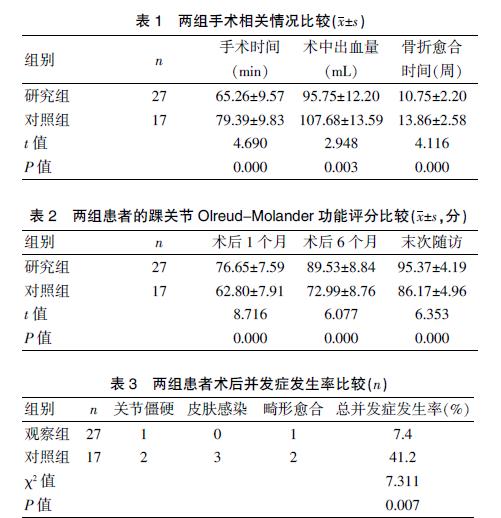
[Abstract] Objective To study the clinical effect of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in the treatment of Pilon fracture. Methods The diagnosis and treatment data of 44 patients with tibial Pilon fracture treated in our hospital from September 2018 to September 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. According to different surgical methods, they were divided into the study group (27 cases) and the control group (17 cases). The control group was treated with traditional incision and internal fixation, while the study group was treated with MIPO technology. The operation time, intraoperative bleeding volume, fracture healing time, Olreud-Molander function score of ankle joint, the incidence of complications and patients′ satisfaction were compared and analyzed between the two groups. Results The operation time, intraoperative bleeding volume and fracture healing time in the study group were (65.26±9.57) min, (95.75±12.20) mL and (10.75±2.20) weeks, respectively, which were significantly lower than those in the control group [(79.39±9.83) min, (107.68±13.59) mL and (13.86±2.58) weeks], with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). The Olreud-Molander scores of ankle joint in the study group were (76.65±7.59) points at 1 month, (89.53±8.84) at 6 months and (95.37±4.19) at the last follow-up, which were significantly higher than those in the control group [(62.80±7.91) points at 1 month, (72.99±8.76) points at 6 months and (86.17±4.96) points at the last follow-up], with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). The incidence rate of postoperative complications such as joint stiffness, skin infection and malunion was lower in the study group (7.4%) than that in the control group (41.2%), and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The postoperative satisfaction was significantly higher in the study group(92.6%) than that in the control group (64.8%), and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion MIPO technique can obviously improve the therapeutic effect in the treatment of Pilon fracture and is worthy of clinical application.