李赟赟


[关键词] 右美托咪定;依托咪酯;胃癌;血流动力学;镇痛
[中图分类号] R735.2 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)19-0136-04
The effect of dexmedetomidine and etomidate on postoperative analgesia after general anesthesia radical surgery for gastric cancer and its influence on infection and hemodynamics
LI Yunyun
Department of Anesthesiology, Qinghai Traffic Hospital, Xi′ning 810000, China
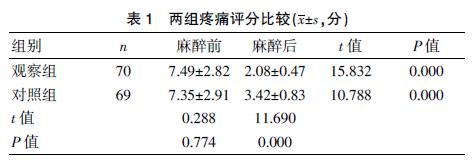
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of dexmedetomidine and etomidate on the postoperative analgesia after general anesthesia radical surgery for gastric cancer and its influence on infection and hemodynamics. Methods In this paper, 139 patients admitted to our hospital from July 2016 to July 2020 were randomly divided into the observation group (n=70) and the control group (n=69). The control group was given etomidate to induce anesthesia. The observation group was anesthetized with dexmedetomidine. The pain score, infection, and hemodynamic changes between the two groups were observed and compared. Results After anesthesia, the pain scores of the two groups decreased significantly (t=11.259, P=0.000; t=8.524, P=0.000). The pain scores of the observation group were significantly lower than those of the control group (t=11.690, P=0.000). The incidence of infection in the observation group was 5.71%, which was significantly lower than the 17.39% in the control group (χ2=4.652, P=0.031). During medication and extubation, the heart rate of the control group was lower than that of the observation group (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (P>0.05). Conclusion Dexmedetomidine and etomidate have a good effect on postoperative analgesia after general anesthesia radical surgery for gastric cancer, which can effectively reduce pain, maintain hemodynamic stability, and reduce the incidence of infection.
[Key words] Dexmedetomidine; Etomidate; Gastric cancer; Hemodynamics; Analgesia
胃癌是临床常见的消化道恶性肿瘤,胃癌根治术是临床治疗胃癌的常用术式,全身麻醉则为手术治疗提供重要基础保障[1]。研究认为,良好的麻醉效果可有效维持患者术中生命体征稳定,减少内环境紊乱所造成的机体应激反应,降低术后感染发生概率[2]。在临床常用麻醉药物中,右美托咪定属于新一代α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂,可有效抑制去甲肾上腺素释放,终止疼痛信号传导;同时抑制交感神经活性,达到镇痛效果[3]。依托咪酯属于非巴比妥类静脉镇静药物,是手术全身麻醉诱导的常用药物[4]。我院于2016年7月~2020年7月共收治胃癌患者139例,所有患者均给予全麻醉根治术治疗,并采用右美托咪定与依托咪酯进行复合麻醉,旨在为此类患者的临床麻醉治疗提供科学理论依据,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选自2016年7月至2020年7月于我院就诊的胃癌全麻醉根治术患者139例,采用随机数字法按1:1比例随机分为观察组(n=70)与对照组(n=69)。观察组,男39例,女31例;年龄36~73岁,平均(57.25±4.48)岁;麻醉时间81~96 min,平均(92.37±2.62)min;手术时间59~86 min,平均(74.19±5.22)min;美国麻醉医师学会(American society of anesthesiologists,ASA)分级:Ⅰ级47例,Ⅱ级23例。对照组,男42例,女27例;年龄38~75岁,平均(57.69±4.54)岁;麻醉时间80~102 min,平均(92.45±2.79)min;手术时间60~84 min,平均(74.08±5.15)min;ASA分级:Ⅰ级48例,Ⅱ级21例。两组患者性别、年龄、麻醉时间、手术时间和ASA分级比较,差异无统计学意义,具有可比性(P>0.05)。