顾晓清 董芹 金少华
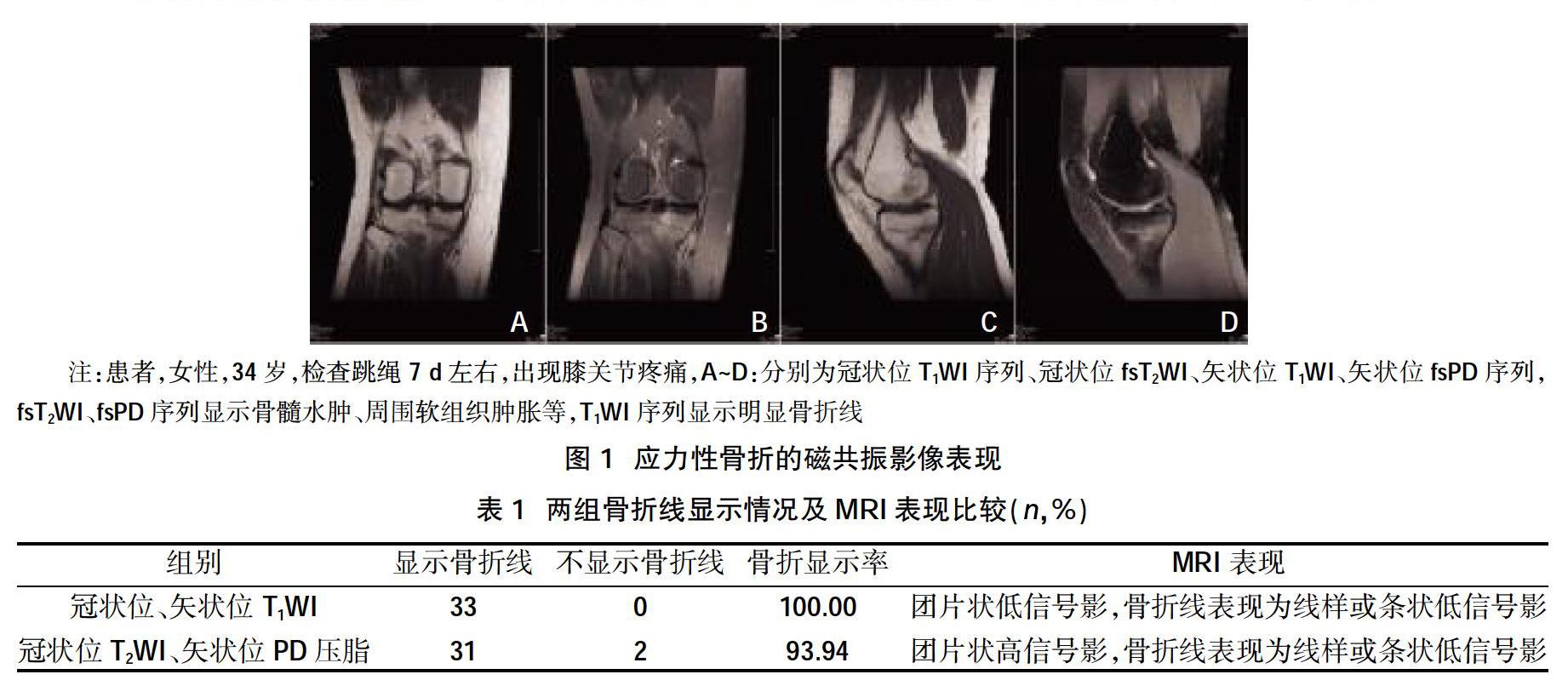
摘要:目的 探讨应力性骨折诊断的磁共振影像表现,分析磁共振成像(MRI)T1WI序列在膝关节应力性骨折中的应用价值。方法 选取2016年1月~2019年12月经临床及随访检查确诊应力性骨折患者34例,行膝关节磁共振检查35例(1例为双侧),按照磁共振序列分为冠状位、矢状位T1WI组和冠状位T2WI、矢状位PD压脂组,分析两组磁共振差异进行。结果 34例患者中膝关节表现为应力性损伤1例,35例应力性损伤均有骨髓水肿信号,其中2例应力性损伤3级,33例应力性损伤4级;两组骨折线走行与皮质垂直或轻度成角;冠状位、矢状位T1WI骨折线显示率(100.00%)高于冠状位T2WI、矢状位PD压脂组骨折线显示率(93.94%)。结论 MRI能显示细微的应力性损伤,并能清晰显示骨折线及软组织情况,冠状位或矢状位T1WI观察骨折线优于T2WI、PD压脂序列。
关键词:膝关节;应力性骨折;应力性损伤;磁共振
中图分类号:R445.2;R684 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.11.054
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)11-0166-02
Abstract:Objective To explore the magnetic resonance imaging manifestation of stress fracture diagnosis and analyze the application value of magnetic resonance imaging T1WI sequence in knee stress fracture.Methods 34 patients with stress fracture diagnosed by clinical and follow-up examination from January 2016 to December 2019 were selected, 35 patients of knee joint magnetic resonance examination (1 case was bilateral), according to the magnetic resonance sequence, it was divided into coronal, sagittal T1WI group and coronal T2WI, sagittal PD lipid pressure group, analysis of the difference between the two groups of magnetic resonance.Results Among the 34 patients, the knee showed 1 case of stress injury, 35 cases of stress injury had bone marrow edema signal, 2 cases of stress injury level 3, 33 cases of stress injury level 4; the fracture line of the two groups was perpendicular to the cortex or slightly angled; the fracture rate of the T1WI fracture line in the coronal and sagittal positions (100.00%) was higher than that in the lipid pressure group of the coronary T2WI,the fracture line display rate (93.94%) in the sagittal PD lipid pressure group.Conclusion MRI can show subtle stress injury, and can clearly show the fracture line and soft tissue, coronal or sagittal T1WI observation fracture line is better than T2WI, PD lipid sequence.
Key words:Knee joint;Stress fracture;Stress injury;Magnetic resonance
应力性骨折(stress fracture)系指长期、反复的外力作用于骨的某一部位,而引起的慢性骨折。随着健身体育运动的广泛开展和保健查体制度的实施,减肥、健身已经成为人们日常活动的一部分。然而不恰当的、过度的运动,必然带来运动损伤,对骨骼施加外在的应力[1]。应力性骨折占运动医学就诊者的10%以上[2]。常规影像技术如X线摄片、CT检查不能明确显示应力性骨折的损伤过程。随着MRI技术的发展,磁共振被广泛应用于慢性损伤影像诊断。在诊断应力性骨折中,MRI已经成为确定应力性骨折诊断的金标准[3]。本研究针对临床诊断的应力性损伤35例,分析其MRI影像分级及损伤特点,膝关节应力性损伤的影像诊断,以及T1WI序列在显示应力性骨折线中的优势,现报道如下。