张德刚 万毅新
脂联素与慢性阻塞性肺病相关性研究
张德刚 万毅新△
目的 研究脂联素与慢性阻塞性肺病(COPD)患者肺功能、年龄、性别的相关性。方法选择COPD急性加重期(急性加重组)和稳定期(稳定组)患者各60例,另择60例健康者为对照组,3组男、女均各30例,采用ELISA法检测血清脂联素,使用肺功能测试仪测量并计算FEV1/FVC、FEV1%预计值和RV/TLC。结果急性加重组总体、男性和女性脂联素水平均高于稳定组和对照组,且稳定组高于对照组(均P<0.05);3组女性脂联素水平均高于男性(均P<0.05)。急性加重组和稳定组FEV1%、FEV1/FVC预计值均低于对照组,且急性加重组和稳定组的RV/TLC均高于对照组(均P<0.05)。急性加重组与稳定组血清脂联素水平与FEV1%预计值、FEV1/FVC均呈负相关,与RV/TLC呈正相关(均P<0.01)。除正常男性血清脂联素与年龄呈正相关(r=0.943,P<0.01)外,其余组二者均无相关性(P>0.05)。结论COPD患者血清脂联素水平明显升高,推测脂联素起促炎作用并与气道阻力有关;血清脂联素存在性别差异,并可能与年龄有关。
脂联素;慢性阻塞性肺病;性别因素;年龄因素;肺功能
慢性阻塞性肺病(COPD)是一种以气流受限为主要特征的疾病,严重影响患者生活质量。脂联素是由脂肪细胞分泌的细胞因子。近年来有关脂联素的研究主要集中在胰岛素抵抗、葡萄糖代谢以及抗动脉粥样硬化等方面,其与COPD相关性的研究较少。脂联素在COPD中起到抗炎作用[1],而Miller等[2]研究发现正常小鼠能够比重症COPD脂联素基因缺陷小鼠诱导出更多的炎性细胞和细胞因子,提示脂联素具有促炎作用。本研究通过分析脂联素与COPD患者肺功能、年龄、性别的相关性,探讨脂联素在COPD炎症中的作用。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象 选取2012年1月—11月在我院呼吸科住院的COPD患者120例,其中急性加重期(急性加重组)和稳定期(稳定组)各60例,另选60例健康者为对照组,3组男、女均各30例。COPD诊断符合中华人民共和国卫生部颁发的慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊断标准(2007版)。体质量指数(BMI)<24 kg/m2。排除标准:(1)严重的心脑血管疾病。(2)严重的肝肾功能损害、肿瘤疾病。(3)肺部以外的感染性疾病。(4)近期使用过激素治疗。(5)近期接受手术治疗。
1.2 试剂与仪器 人血脂联素ELISA分析试剂盒(批号:201209)购自西安科昊生物工程有限责任公司。美国BIORAD680酶标仪。KDC-2046低温大容量离心机(中国科学技术大学科技实业总公司中佳光电仪器分公司),恒温水浴箱、加样枪、枪头等。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 血清脂联素的测定 空腹采肘正中静脉血4 mL,以3 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液,置于4℃的冰箱保存待测,严格按照ELISA试剂盒操作步骤进行检测。
1.3.2 肺功能指标测定 使用肺功能测试仪(德国耶格公司Master Screen肺功能检测系统)测量第1秒用力呼气容积(FEV1),用力肺活量(FVC),残气量(RV)和肺总量(TLC),计算FEV1/FVC、FEV1%预计值和RV/TLC。
1.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计处理,计量资料以±s表示,两独立样本比较采用t或t’检验;多组间比较行one-way ANOVA,组间多重比较采用LSD-t检验。相关性分析采用Pearson相关,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 3组一般资料比较 3组年龄、BMI、收缩压、舒张压、空腹血糖差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05),见表1。
Table 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between three groups表1 3组一般资料比较 (n=60,±s)
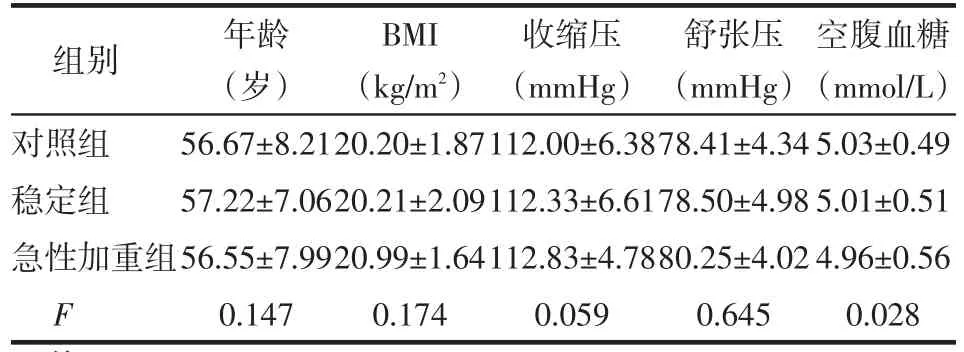
Table 1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between three groups表1 3组一般资料比较 (n=60,±s)
均P>0.05;1 mmHg=0.133 kPa
组别对照组稳定组急性加重组F年龄(岁)56.67±8.21 57.22±7.06 56.55±7.99 0.147 BMI(kg/m2)20.20±1.87 20.21±2.09 20.99±1.64 0.174收缩压(mmHg)112.00±6.38 112.33±6.61 112.83±4.78 0.059舒张压(mmHg)78.41±4.34 78.50±4.98 80.25±4.02 0.645空腹血糖(mmol/L)5.03±0.49 5.01±0.51 4.96±0.56 0.028
2.2 各组间脂联素水平的比较 急性加重组总体、男性和女性脂联素水平均高于稳定组和对照组,且稳定组也高于对照组(均P<0.05);3组女性脂联素水平均高于男性(均P<0.05),见表2。
2.3 各组不同性别间肺功能指标的比较 急性加重组男、女性FEV1%预计值均低于稳定组和对照组,且稳定组也低于对照组(均P<0.05)。急性加重组和稳定组男、女性FEV1/FVC均低于对照组(均P<0.05);急性加重组女性FEV1/FVC低于稳定组,2组间男性FEV1/FVC差异无统计学意义。急性加重组男、女性RV/TLC均高于稳定组和对照组,且稳定组也高于对照组(均P<0.05),见表3、4。
Table 2 Comparison of adiponectin levels between three groups表2 各组间和组内不同性别间脂联素水平的比较(mg/L,±s)
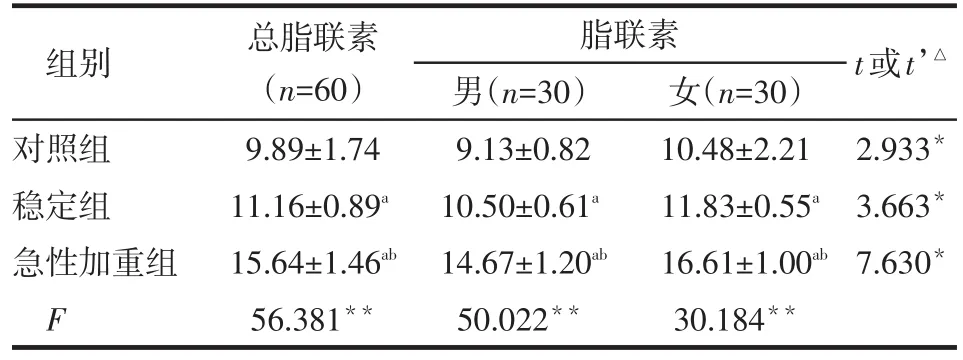
Table 2 Comparison of adiponectin levels between three groups表2 各组间和组内不同性别间脂联素水平的比较(mg/L,±s)
*P<0.05,**P<0.01;a与对照组比较,b与稳定组比较,P<0.05;表3、4同;△表示各组内男、女脂联素水平比较t或t’值
组别对照组稳定组急性加重组F总脂联素(n=60)9.89±1.74 11.16±0.89a15.64±1.46ab56.381**脂联素男(n=30)9.13±0.82 10.50±0.61a14.67±1.20ab50.022**女(n=30)10.48±2.21 11.83±0.55a16.61±1.00ab30.184**t或t’△2.933*3.663*7.630*
Table 3 Comparison of lung function index between three groups表3 各组男性肺功能指标的比较 (n=60±s)
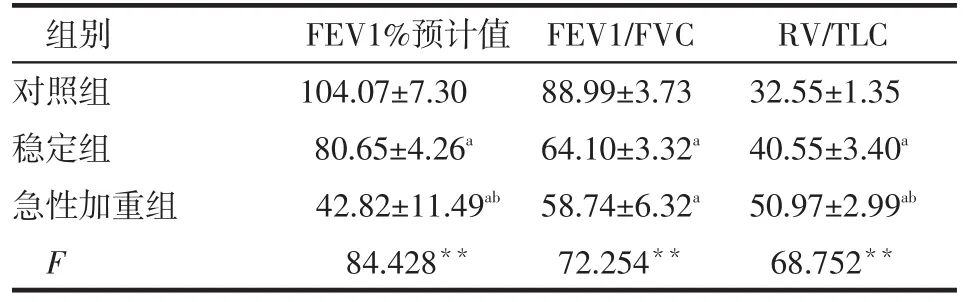
Table 3 Comparison of lung function index between three groups表3 各组男性肺功能指标的比较 (n=60±s)
组别对照组稳定组急性加重组F FEV1%预计值104.07±7.30 80.65±4.26a42.82±11.49ab84.428**FEV1/FVC 88.99±3.73 64.10±3.32a58.74±6.32a72.254**RV/TLC 32.55±1.35 40.55±3.40a50.97±2.99ab68.752**
Table 4 Comparison of lung function index between three groups表4 各组女性肺功能指标的比较 (n=60±s)
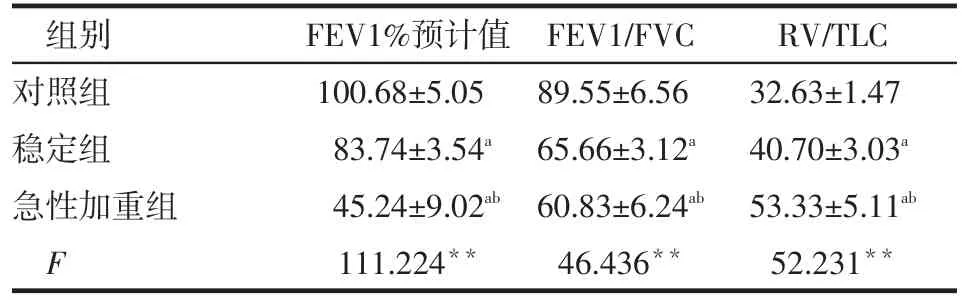
Table 4 Comparison of lung function index between three groups表4 各组女性肺功能指标的比较 (n=60±s)
组别对照组稳定组急性加重组F FEV1%预计值100.68±5.05 83.74±3.54a45.24±9.02ab111.224**FEV1/FVC 89.55±6.56 65.66±3.12a60.83±6.24ab46.436**RV/TLC 32.63±1.47 40.70±3.03a53.33±5.11ab52.231**
2.4 COPD患者血清脂联素水平与肺功能指标的相关性 急性加重组与稳定组患者血清脂联素水平与FEV1%预计值(r1=-0.839,r2=-0.762)、FEV1/FVC(r1=-0.633,r2=-0.651)均呈负相关,与RV/TLC呈正相关(r1=0.846,r2=0.742),均P<0.01。
2.5 各组男、女年龄与脂联素水平的相关性 除对照组男性年龄与脂联素水平呈正相关(P<0.01)外,其余组年龄与脂联素水平均无相关性(均P>0.05),见表5。
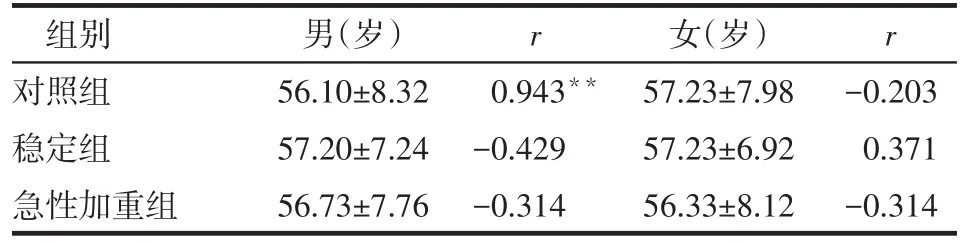
Table 5 The correlation analysis between indicators of age and adiponectin levels in three groups表5 各组男、女年龄与脂联素水平的相关性分析
3 讨论
Daniele等[3]采用ELISA技术、Western blot发现COPD患者血清脂联素能够抑制诸如肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α等促炎因子的释放,起到保护性作用,推测脂联素作为抗炎因子,参与COPD的发病过程。Miller等[4]研究发现,脂联素可与气道表皮和巨噬细胞诱导性的脂联素受体1结合,促进白细胞介素(IL)-8、TNF-α等炎性介质的产生,趋化多种炎性细胞(巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞等)聚集。IL-8的分泌和合成进一步促进脂联素的合成和诱导气道上皮细胞和巨噬细胞再次产生脂联素受体1,通过自分泌和旁分泌的方式产生级联放大效应起到抗炎作用。田银君等[5]通过分析老年COPD患者血浆脂联素水平发现,COPD稳定期患者血浆脂联素水平较急性加重期和对照组高,进一步证实脂联素的抗炎作用。但本研究结果显示,急性加重组和稳定组患者血清脂联素水平明显高于对照组,且急性加重组高于稳定组,提示血清脂联素可能是一种新型的促炎因子,参与COPD的慢性炎症过程;这与谢娟等[6]的研究结果是一致的,并推测脂联素也可能通过IL-17起到促炎作用。
COPD是一种以气流受限为特征的肺部疾病,气流受限不完全可逆,呈进行性发展。本研究结果发现急性加重期和稳定期患者血清脂联素水平均与FEV1%预计值、FEV1/FVC呈负相关,与RV/TLC呈正相关,提示血清脂联素水平与气道阻力有关。有研究提出骨骼肌细胞可表达脂联素受体1,能够促进葡萄糖摄取及脂质氧化;COPD患者特别是急性加重期患者,存在过度通气、呼吸运动负荷加重、血清脂联素及脂联素受体1表达增高等现象[7]。
目前,有关COPD患者血清脂联素的性别差异研究较少。本研究结果表明,3组女性脂联素水平均高于男性,提示COPD患者的脂联素水平存在性别差异,其原因多因雌雄激素差异所致。Cicero等[8]通过比较绝经期后妇女与男性血清脂联素水平,发现此差异仍存在,故认为雌激素不能解释脂联素的性别差异,而可能与雄激素抑制血浆脂联素合成分泌有关。但Gui等[9]研究发现,雄性小鼠去势后并不影响血浆脂联素的性别差异。目前关于血浆脂联素性别差异的原因,尚需进一步研究。
Isobe等[10]对1 519例北海道居民(其中男964例,女592例)进行血清脂联素检测结果发现,男性和小于50岁女性的血清脂联素水平均与年龄呈正相关。本研究中除对照组男性血清脂联素水平与年龄呈正相关外,其余组脂联素水平与年龄均无相关性,本研究与Isobe等[10]研究结果不一致的可能原因在于选取对象的年龄、体内性激素的变化(特别是女性绝经前后雌激素的变化)及COPD炎症本身所致。Mallamaci等[11]研究发现,肾肌酐清除率下降与血清脂联素呈负相关,推测肾脏清除率下也是导致老年患者血浆脂联素水平升高的原因之一。其他可能的机制还需进一步研究探讨。
[1]Chan KH,Yeung SC,Yao TJ,et al.Elevated plasma adiponectin levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J].Int J Tuberc Lung Dis,2010,14(9):1193-1200.
[2] Miller M,Pham A,Cho JY,et al.Adiponectin-deficient mice are protected against tobacco-induced inflammation and increased emphysema[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2010,299(6):L834-L842.
[3] Daniele A,De Rosa A,Nigro E,et al.Adiponectin oligomerization state and adiponectin receptors airway expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J].Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2012,44(3): 563-569.
[4]Miller M,Cho JY,Pham A,et al.Adiponectin and functional adiponectin receptor 1 are expressed by airway epithelial cell in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J].J Immunol,2009,182(1):684-691.
[5]田银君,刘前桂,赵黎,等.老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血浆脂联素水平[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(13):2424-2426.
[6]谢娟,邓星奇,龙威,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血浆脂联素水平及其与白介素17的相关性[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2011,10(1):21-24.
[7]程珺,文重远.追赶生长大鼠脂联素及其受体与胰岛素抵抗的相关性研究[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(16):2934-2936.
[8]Cicero AF,Magni P,Lentini P,et al.Sex hormones and adipokines in healthy pre-menopausal,post-menopausal and elderly women,and in age-matched men:Data from the Brisighella Heart Study[J]. J Endocrinol Invest,2011,34(7):e158-e162.
[9]Gui Y,Silha JV,Murphy LJ.Sexual dimorphism and regulation of resistin,adiponectin,and leptin expression in the mouse[J].Obes Res, 2004,12(9):1481-1491.
[10]Isobe T,Saitoh S,Takagi S,et al.Influence of gender,age and renal function on plasma adiponectin level:the Tanno and Sobetsu study [J].Eur J Endocrinol,2005,153(1):91-98.
[11]Mallamaci F,Zoccali C,Cuzzola F,et al.Adiponectin in essential hypertension[J].J Nephrol,2002,15(5):507-511.
(2013-04-30收稿 2013-06-24修回)
(本文编辑 陈丽洁)
Correlation of Adiponectin and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
ZHANG Degang,WAN Yixin
Department of Respiratory,the Second Affiliated Hospital of Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730000,China
ObjectiveTo study the relationship between adiponectin and pulmonary function,age and gender in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD).MethodsA total of 120 COPD patients with normal body mass index(BMI<24 kg/m2)were selected and divided into acute exacerbation group(n=60)and stable group(n=60).And 60 healthy people were included as controls.There were equal numbers of male and female in each group.The serum level of adiponectin was sdetected by ELISA in there groups.The pulmonary function was collected,and values of FEV1/FVC, FEV1%predicted and RV/TLC were calculated in three groups.ResultsThe serum level of adiponectin was significantly higher in acute exacerbation group than that of stable group and control group(P<0.05).And the serum level of adiponectin was significantly higher in stable group than that of control group(P<0.05).The serum levels of adiponectin were significantly higher in female patients than those of male patients(P<0.05).The values of FEV1%,FEV1/FVC and FEV1%predicted were significantly lower in acute exacerbation group and stable group than those of control group.The value of RV/ TLC was significantly higher in acute exacerbation group and stable group than that of control group(P<0.05).There was a negative correlation in serum levels of adiponectin,FEV1%predicted and FEV1/FVC between acute exacerbation group and stable group.But there was a negative correlation in serum levels of adiponectin and RV/TLC between these two groups(P<0.01).There was a positive correlation between serum level of adiponectin and age in male patients(r=0.943,P<0.01).ConclusionThe serum level of adiponectin was significantly increased in patients with COPD,which suggested that adiponectin played an important part in proinflammatory and might be closely related with airway resistance.The serum level of adiponectin might exist gender differences and may be related with age.
adiponectin;chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;sex factors;age factors;pulmonary function
R563.5
A【DOI】10.3969/j.issn.0253-9896.2014.01.012
兰州大学第二医院呼吸科(邮编730000)
△通讯作者 E-mail:wanyixin@yahoo.com.cn