柴 利,黄 娟,陈 明,杨志惠
(西南医科大学附属医院病理科,四川泸州 646000)
论着·临床研究 doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.30.012
TLR基因多态性与结直肠癌易感性*
柴 利,黄 娟,陈 明,杨志惠△
(西南医科大学附属医院病理科,四川泸州 646000)
目的 检测Toll样受体2(TLR2)R753Q和Toll样受体4(TLR4)D299G、T399I多态性,分析其在结直肠癌发生、发展中的作用及机制。方法 收集结直肠癌患者及健康对照者各256例。R753Q、D299G和T399I位点基因型检测采用聚合酶链式反应-限制性片段长度多态性(PCR-RFLP)分析方法。结直肠癌组织中白细胞介素(IL)-1α、IL-8、巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-1α(MIP-1α)、单核细胞趋化因子-1(MCP-1)蛋白水平检测采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)。结果 TLR4 T399I与结直肠癌发病风险相关。CT合并TT基因型在病例组中频率为31.2%,在对照组中仅为18.7%;T等位基因在病例组和对照组中频率分别为18.2%和10.2%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);T399I T等位基因个体患结直肠癌风险明显增加(OR=2.534,95%CI:1.462~2.734,P<0.01)。不同基因型个体结直肠癌组织中IL-1α和MCP-1表达水平有明显差异。CT合并TT基因型个体肿瘤组织中 IL-1α水平为(36.97±21.43)pg/mg,而CC基因型个体为(22.27±17.89)pg/mg;MCP-1水平在CT合并TT基因型个体中为(24.57±17.74)pg/mg,而CC基因型个体为(12.91±9.78)pg/mg。结论 TLR4 T399I与结直肠癌的发生、发展有关,T等位基因个体患结直肠癌的风险明显增加,其机制可能是通过调控IL-1α和MCP-1在结直肠癌组织中的表达。
Toll样受体;结直肠癌;多态性;细胞因子;趋化因子
Toll样受体家族(Toll-like receptors,TLRs)是一个模式识别受体家族,目前已经被确认的人类TLR 有11个。来源不同的微生物,如细菌、病毒、原虫和真菌的分子模式被TLR识别[1]。近年研究发现,不仅在人类免疫相关细胞上,在正常胃黏膜、肠黏膜、生殖道和呼吸道等上皮细胞中均有TLRs表达[2-5]。TLRs与慢性炎症性疾病及肿瘤的发生、发展有关,但其分子机制尚不清楚[6-9]。本研究通过分析Toll样受体2(Toll-like receptor 2,TLR2)R753Q,Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)D299G和T399I 基因型在结直肠癌病例-对照组中的分布,探讨其与结直肠癌发病风险的相关性,并分析不同基因型个体结直肠癌组织中细胞因子和趋化因子蛋白的表达。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 收集2012~2014年本院胃肠外科及肿瘤科结直肠癌初诊患者256例(病例组),另外健康对照个体256例为本院同期健康体检者(对照组)。所有研究对象均为无血缘关系的汉族个体,排除心、脑、肾及其他器官系统疾病。两组性别、年龄、吸烟状况等分布差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 基因型检测 引物序列如下[10-11]:D299G: 5′-TTA GAA ATG AAG GAA ACT TGG AAA AG-3′和5′-TTT GTC AAA CAA TTA AAT AAG TGA TTA ATA-3′;T399I:5′-GGT TGC TGT TCT CAA AGT GAT TTT GGG AGA A-3′和 5′-CCT GAA GAC TGG AGA GTG AGT TAA ATG CT-3′;R753Q :5′ -TAT GGT CCA GGA GCT GGA GA-3′ 和 5′ -TGA CAT AAA GAT CCC AAC TAG ACA A-3′。聚合酶链式反应(PCR)总反应体系均为25 μL,上游引物及下游引物均为0.4 μL,2×PCR 混合物12.5 μL,DNA模板2 μL,双蒸水补足25 μL。反应条件:95 ℃ 4 min,94 ℃ 45 s,55 s(D299G:56 ℃,R753Q和T399I:58 ℃),72 ℃延伸1 min,35个循环,最后72 ℃延伸10 min。采用Bio-Rad热循环仪进行。各基因位点 PCR产物10 μL,分别经BsaBI,HinfI和SfcI 5 U 37 ℃过夜消化。酶切产物点样于6%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶,600 V 1 h电泳,银染显色。
1.2.2 癌组织细胞因子及趋化因子蛋白浓度检测 结直肠癌新鲜活体组织55份,T399I CT或TT基因型为一组,基因型CC为一组,分别为25、30份。肿瘤组织匀浆中白细胞介素(IL)-1α、巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-1α(macrophage inflammatory protein-1α,MIP-1α)、IL-8和单核细胞趋化因子-1(monocyte chemotactic protein-1,MCP-1)蛋白表达采用酶链免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测。试剂盒由Invitrogen公司提供,检测按试剂盒说明书操作。每份样品检测两次,取均值。
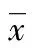
2 结 果
2.1 TLR基因多态性与结直肠癌相关性分析 D299G、T399I和R753Q多态性位点基因型分布符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡定律(P>0.05)。D299G和R753Q基因型及等位基因频率分布无差异(结果未显示)。CT合并TT基因型在病例组中频率为31.2%,在对照组中仅为18.7%;T等位基金在病例组和对照组中频率分别为18.2%和10.2%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。T399I T等位基因的个体患结直肠癌风险明显增加(OR=2.534,95%CI:1.462~2.734,P<0.01),见表1。
2.2 TLR基因多态性与结直肠癌临床病理参数分层分析 分层分析结果显示,D299G、T399I和R753Q多态性在临床Ⅰ+Ⅱ期和Ⅲ+Ⅳ期中频率分布差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);在高、中、低分化肿瘤各组中的频率分布差异亦无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表2。且TLR基因多态性与性别、年龄、吸烟状况等无交互作用(结果未显示)。
2.3 TLR基因多态性与结直肠癌组织中细胞因子和趋化因子浓度相关性分析 IL-8和MIP-1α在T399I CT或TT基因型个体组及CC基因型个体组中的表达差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。IL-1α在25例CT合并TT基因型个体中表达水平为(36.97±21.43)pg/mg,高于在30例CC基因型个体中的表达水平[(22.27±17.89)pg/mg];MCP-1在CT合并TT基因型个体的表达水平[(24.57±17.74) pg/mg]亦高于CC基因型个体[(12.91±9.78)pg/mg]。IL-1α和MCP-1在T399I不同基因型中的表达水平比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),IL-1α和MCP-1浓度与个体基因型相关,见图1。
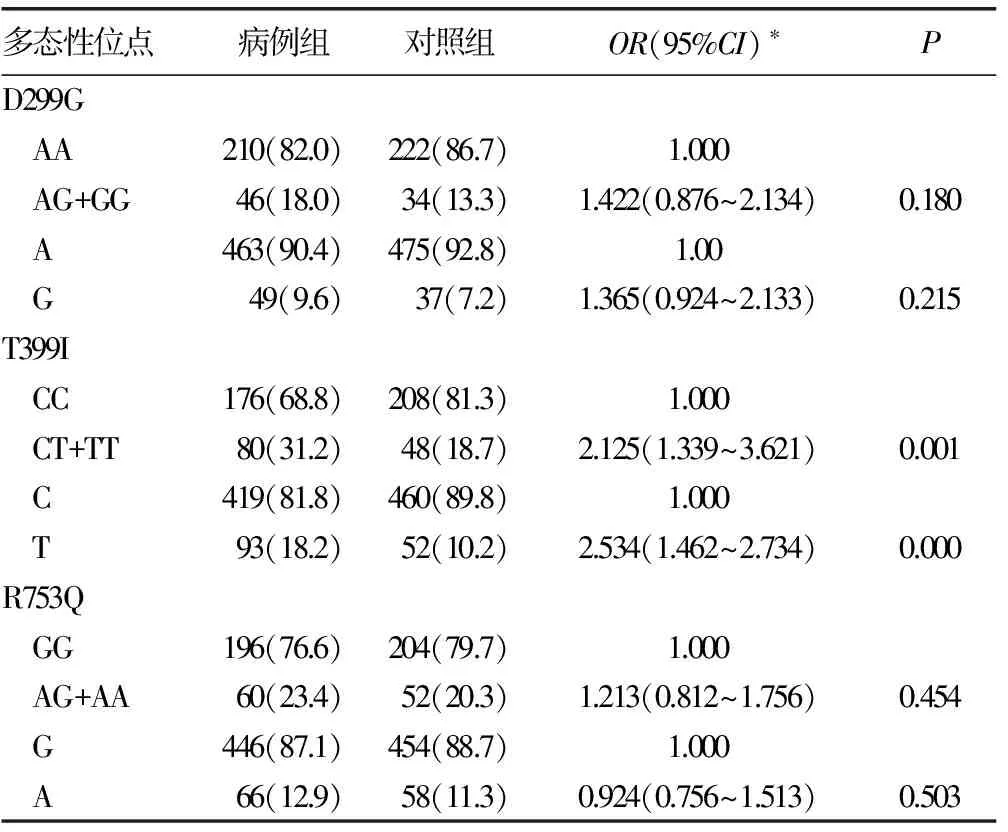
表1 TLR 基因多态性基因型分布及与其结直肠癌相关性分析[n=256,n(%)]
*:性别和年龄校正OR和95%CI。
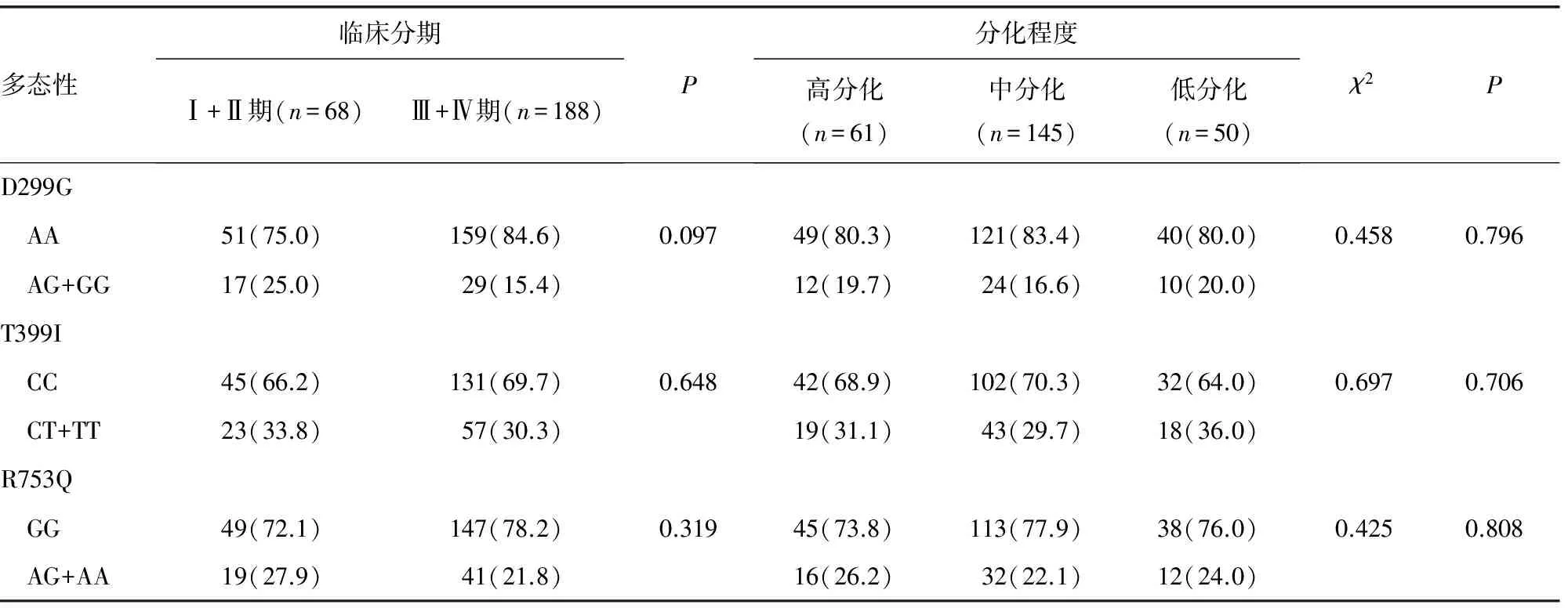
表2 TLR多态性与结直肠癌临床病理参数分层分析[n(%)]
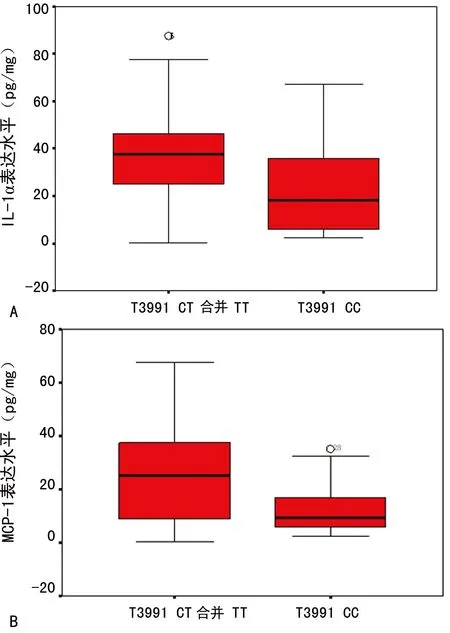
A:IL-1α表达水平比较;B:MCP-1表达水平比较。
图1 不同基因型个体肿瘤组织中IL-1α 和MCP-1表达水平比较
3 讨 论
结直肠癌是最常见的消化道系统恶性肿瘤,其发生与个人饮食、遗传、环境等因素有关。而环境因素致癌最终取决于个人对肿瘤的易感性。本文探讨了TLR2 R753Q和TLR4 D299G、T399I多态性与大肠腺癌的关系,探索该遗传多态性位点在结直肠癌发生、发展中的作用及可能的机制,拟为结直肠癌的防控提供基础科研依据。结果显示,TLR4 T399I与结直肠癌的发病风险相关。T399I T等位基因的个体患结直肠癌患病风险明显增加(OR=2.534,95%CI:1.462~2.734,P<0.01)。不同基因型个体结直肠癌组织中IL-1α和MCP-1表达有明显差异。IL-1α和MCP-1在CT合并TT基因型个体的肿瘤组织中表达水平均明显高于CC基因型个体组。
近年研究发现,肿瘤形成的主要原因之一是肿瘤细胞具有逃避宿主免疫系统识别及清除的能力。TLRs是参与非特异性免疫的一类重要分子,也是连接天然免疫和获得性免疫系统的重要桥梁,在免疫系统中有着极为特殊的地位[12]。TLRs不仅能识别病原相关分子模式配体(pathogen associated molecular patterns,PAMPs),还能识别并结合机体自身产生的热休克蛋白、坏死细胞释放的核苷酸和DNA等内源性分子即内源性配体,进行信号转导,调节细胞因子的分泌而发挥生物学效应。TLRs主要表达在人类免疫相关细胞上,但在人类正常上皮及一些肿瘤细胞如宫颈癌、胃癌细胞中也发现高表达,并且与肿瘤生成、演变和侵袭进展有关[13-15]。
TLR4的配体是细菌脂多糖及其他肿瘤产物,结直肠中存在大量病原微生物,甚至有肿瘤细胞产物。TLR4可识别结直肠中的这些配体而启动受体后信号传导途径,调节细胞因子和趋化因子的表达,改变肿瘤微环境,促进肿瘤逃避免疫监视,促进肿瘤的发展。本研究证实了TLR4可调节结直肠癌组织中IL-1α和MCP-1的表达,影响肿瘤的发生。而TLR4个体基因型不同,可影响其对配体的敏感性,从而个体患结直肠癌的风险亦有差异。
[1]Akira S,Uematsu S,Takeuchi O.Pathogen recognition and innate immunity[J].Cell,2006,124(4):783-801.
[2]Furrie E,Macfarlane S,Thomson G,et al.Toll-like receptors-2,-3 and -4 expression patterns on human colon and their regulation by mucosal-associated bacteria[J].Immunology,2005,115(4):565-574.
[3]Schmausser B,Andrulis M,Endrich S,et al.Expression and subcellular distribution of toll-like receptors TLR4,TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection[J].Clin Exp Immunol,2004,136(3):521-526.
[4]Huhta H,Helminen O,Kauppila JH,et al.The expression of Toll-like receptors in normal human and murine gastrointestinal organs and the effect of microbiome and cancer [J].J Histochem Cytochem,2016,64(8):470-482.
[5]Liu W,Chen M,Li X,et al.Interaction of Toll-like receptors with the molecular chaperone Gp96 is essential for Its activation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response[J].PLoS One,2016,11(5):e0155202.
[6]Chuang HC,Huang CC,Chien CY,et al.Toll-like receptor 3-mediated tumor invasion in head and neck cancer[J].Oral Oncol,2012,48(3):226-232.
[7]曾红梅,潘凯枫,张阳,等.ToⅡ样受体2及ToU样受体9基因多态性与胃癌易感性的关系[J].中华预防医学杂志,2011,45(7):588-592.
[8]陈晓,王启之,梁冰,等.Toll 样受体4、肿瘤坏死因子-α 在溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠组织中的表达及意义[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2013,38(2):134-136.
[9]Schwartz AL,Dickerson E,Dagia N,et al.TLR signaling inhibitor,phenylmethimazole,in combination with tamoxifen inhibits human breast cancer cell viability and migration[J/OL].Oncotarget,2016[2016-09-28].http://www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/index.php?journal=oncotarget&page=article&op=view&path%5B%5D=10358.doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10358.
[10]Rigoli L,Di Bella C,Fedele F,et al.TLR4 and NOD2/CARD15 genetic polymorphisms and their possible role in gastric carcinogenesis[J].Anticancer Res,2010,30(2):513-517.
[11]Speletas M,Kalala F,Mitroulis I,et al.TLR2 and TLR4 polymorphisms in familial Mediterranean fever[J].Hum Immunol,2009,70(9):750-753.
[12]Medzhitov R,Preston-Hurlburt P,Janeway CA Jr.A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity[J].Nature,1997,388(6640):394-397.
[13]Chen R,Alvero AB,Silasi DA,et al.Cancers take their Toll-the function and regulation of Toll-like receptors in cancer cells[J].Oncogene,2008,27(2):225-233.
[14]Li W,Xiao J,Zhou X,et al.STK4 regulates TLR pathways and protects against chronic inflammation-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J].J Clin Invest,2015,125(11):4239-4254.
[15]Dong T,Yi T,Yang M,et al.Co-operation of α-galactosylceramide-loaded tumour cells and TLR9 agonists induce potent anti-tumour responses in a murine colon cancer model[J].Biochem J,2016,473(1):7-19.
The correlation of genetic polymorphism of Toll-like receptor with susceptibility of colorectal carcinoma*
Chai Li,Huang Juan,Chen Ming,Yang Zhihui△
(DepartmentofPathology,theAffiliatedHospitalofSouthwestMedicalUniversity,Luzhou,Sichuan646000,China)
Objective To detect genetic polymorphism of Toll like receptor 2(TLR2) R753Q and Toll like receptor 4(TLR4) D299G and T399I,and to analyze its role and mechanism in the occurrence and development of colorectal carcinoma.Methods Totally 256 cases of patients with colorectal carcinoma and 256 cases of healthy control individuals were collected.The genotypes of TLR2 R753Q,TLR4 D299G and TLR4 T399I were detected by using PCR-RFLP method.The levels of IL-1α,IL-8,MIP-1α and MCP-1 protein were detected by using ELISA.Results It is shown that TLR4 T399I was associated with the risk of colorectal cancer.The frequency of CT combined TT genotype of T399I in case group and control group was 31.2% and 18.7%,respectively.The frequency of T allele in case group and control group was 18.2% and 10.2%,respectively,and difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Individuals with T allele of T399I showed a 2.534-fold increase in colorectal cancer risk compared with the T399I C allele(95%CI:1.462-2.734,P<0.01).There were significant differences in the expression levels of IL-1α and MCP-1 in colorectal carcinoma tissues of different genotypes.The expression level of IL-1α in patients with CT combined TT genotype of T399I and those with CC genotype was (36.97±21.43) and (22.27±17.89)pg/mg respectively,and the expression level of MCP-1 was (24.57±17.74) and (12.91±9.78)pg/mg respectively.Conclusion T399I TLR4 is associated with the occurrence and development of colorectal carcinoma,and the risk of colorectal carcinoma in individuals with T genotype is significantly increased,in which monitoring the expression of IL-1 and MCP-1 in colorectal carcinoma tissues might be the mechanism.
Toll like receptor;colorectal cancer;polymorphism;cytokine;chemokine
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81101679);四川省科技厅基金资助项目(14JC0091);四川省泸州市基金资助项目(2013LZLY-J44)。 作者简介:柴利(1970-),技师,大专,主要从事消化道肿瘤病理学研究。△
R363.2+5
A
1671-8348(2016)30-4214-03
2016-03-03
2016-06-16)