滕长财,郑红
12种microRNA在卵巢癌中的表达及临床意义
滕长财,郑红
目的利用公共数据库分析卵巢癌组织中12种microRNA(miR)的表达及其临床意义。方法筛选在GSE14407数据集和TCGA数据库中均具有表达信息的microRNA,得到miR-10B、miR-1244、miR-622、miR-21、miR-503、Let-7D、miR-155、miR-30C、miR-17、miR-101-1、miR-186以及miR-770共12种microRNA,在这12种microRNA中寻找在卵巢癌(卵巢癌组)和癌旁组织(癌旁组)中表达有差异的基因。利用在TCGA数据库中筛选得到的505例卵巢癌患者数据,年龄按照中位数分为高年龄( 59岁)组和低年龄(<59岁)组;临床分期分为早期组(Ⅰ期+Ⅱ期)、晚期组(Ⅲ期+Ⅳ期)及未知;肿瘤分级分为低级别(G1+G2)组和高级别(G3+G4)组;病发位置分为单侧组、双侧组;肿瘤残余分为<10 mm组、 10 mm组;microRNA按照表达量的中位数分为高表达组和低表达组,进行Kaplan-Meier单因素生存分析和多因素Cox回归分析。结果癌旁组Let-7D和miR-101-1表达水平高于卵巢癌组,而miR-155和miR-770表达水平低于卵巢癌组(均P<0.05)。生存分析显示,年龄 59岁、临床分期(Ⅲ+Ⅳ)期和Let-7D低表达的患者生存情况较差(P<0.05)。Let-7D低表达是卵巢癌患者生存的独立危险因素。结论Let-7D的表达与卵巢癌预后相关,可能是卵巢癌预后的独立影响指标。
卵巢肿瘤;因素分析,统计学;微RNAs;预后;GEO数据库;TCGA数据库;Let-7D
卵巢癌复发率高且5年生存率低,已经成为致死率最高的妇科肿瘤[1]。据统计,2012年美国新增卵巢癌病例约有2万例,并且每年有约1.5万例患者死于卵巢癌[2]。卵巢癌发病隐匿,早期缺乏典型的临床症状,再加上其特殊的生理位置导致诊断困难,因此,卵巢癌患者一旦发现大多处于中晚期。众所周知,某些microRNA(miR)可以调节癌基因和抑癌基因的表达,进而调控肿瘤的发生发展。本课题组前期研究显示,血浆中的miR-205和Let-7f联合诊断可以提高卵巢癌的诊断率,同时Let-7f高表达的患者预后较好[3]。另有大量研究显示miR-217[4]、miR-125A/125B[5]、miR-613[6]及miR-181C[7]均能通过靶向不同的基因,对卵巢癌的进展起到抑制作用;而另有研究显示,miR-144可通过靶向Glut1基因来改变卵巢癌细胞的代谢方式,促进卵巢癌细胞的生长[8]。因此,为了得到更多与卵巢癌进展相关的microRNA,以便为以后个体化治疗提供生物学基础,本研究利用基因表达综合数据库(gene expression omnibus,GEO)和癌症基因组图谱(the cancer genome atlas,TCGA)中的卵巢癌患者数据分析12种microRNA的表达与临床特征及预后的关系。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料GEO数据库属于美国生物技术信息中心,是全球最大的生物数据库之一。笔者从GEO数据库中筛选含有卵巢癌和癌旁组织基因表达信息的数据集,发现数据集
GSE14407[9]包含卵巢癌和癌旁组织的基因表达数据,其中包含12例卵巢上皮细胞组织(癌旁组)和12例上皮源浆液性卵巢癌组织(卵巢癌组)数据。TCGA数据库是目前最大的癌症生物信息数据库,包含了大量的生物医学信息,笔者从中选取卵巢癌患者的microRNA表达数据和临床数据,并根据年龄、肿瘤分级、病发位置、临床分期和肿瘤残余等临床信息的完整程度,在TCGA数据库中筛选得到505例卵巢癌患者资料用于分析研究。本文所下载数据截止时间均为2015年9月22日。
1.2方法首先,筛选在GSE14407数据集和TCGA数据库中均具有表达信息的microRNA,得到miR-10B、miR-1244、miR-622、miR-21、miR-503、Let-7D、miR-155、miR-30C、miR-17、miR-101-1、miR-186及miR-770共12种microRNA。对GSE14407数据集中的表达值进行数据转换,取以10为底的log对数,进而分析12种microRNA在卵巢癌组和癌旁组中的表达情况,找出具有表达差异microRNA。利用TCGA数据库中的505例卵巢癌患者的信息,对有表达差异的microRNA进行单因素和多因素生存分析,找到具有临床意义的microRNA。505例卵巢癌患者的生存期(OS)定义为从诊断到死亡的生存时间,随访时间0~183个月,中位数是30个月。将505例卵巢癌患者的临床资料依年龄、美国癌症联合委员会(American Joint Committee on Cancer,AJCC)癌症临床分期、美国国家综合癌症网络(National Comprehensive Cancer Network,NCCN)肿瘤分级、肿瘤病发位置、术后肿瘤残余等进行分类纳入生存分析。年龄按照中位数分为高年龄(59岁)组和低年龄(<59岁)组;临床分期分为早期组(Ⅰ期+Ⅱ期)、晚期组(Ⅲ期+Ⅳ期)及未知;肿瘤等级分为低级别组(G1+G2)、高级别组(G3+G4);病发位置分为单侧组、双侧组;肿瘤残余分为<10 mm组、 10 mm组;microRNA按照表达量的中位数分为高表达组和低表达组。
1.3统计学方法采用Graphpad 5.0软件和SPSS 21.0软件进行统计分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x ±s表示,2组间均数比较采用t检验。生存分析采用Kaplan-Meier法,Log-Rank分析生存差异。运用Cox比例风险回归模型分析卵巢癌患者的生存影响因素,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 12种microRNA在卵巢癌和癌旁组织中的表达情况癌旁组Let-7D和miR-101-1表达水平高于卵巢癌组,而miR-155和miR-770低于卵巢癌组(均P<0.05),见表1。
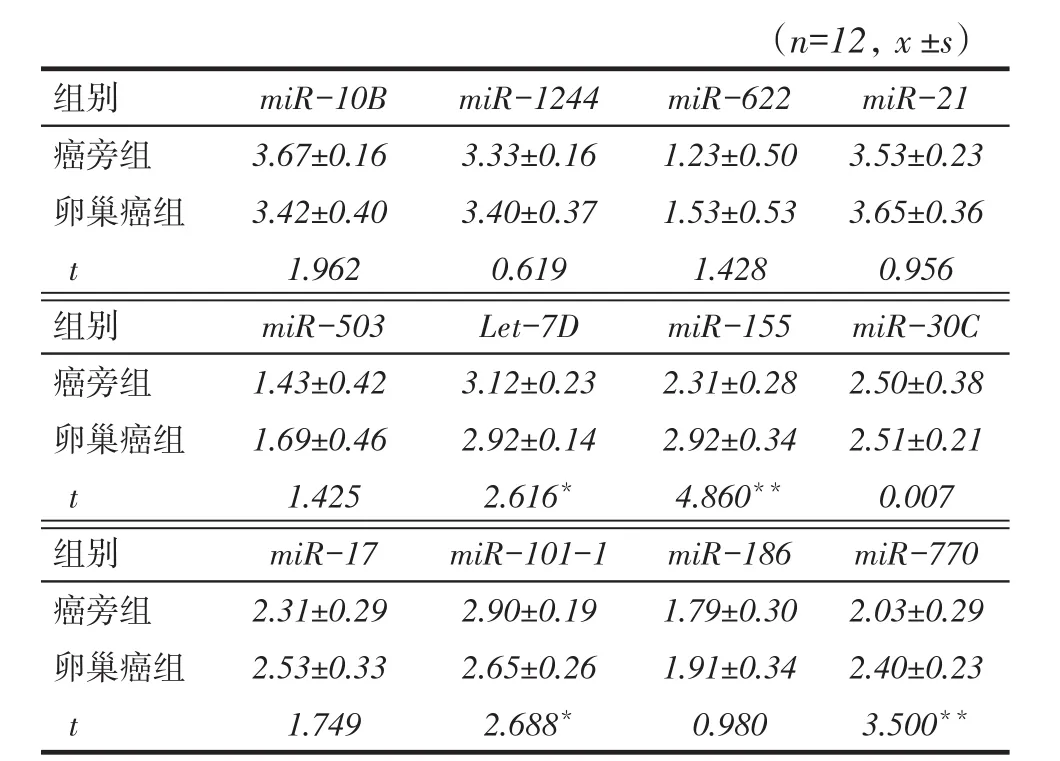
Tab. 1 The expression levels of 12 kinds of microRNAs in ovarian carcinoma and paracancerous tissue表1 12种microRNA在卵巢癌和癌旁组织的表达情况
2.2生存分析年龄 59岁、临床分期晚[(Ⅲ+Ⅳ)]期和Let-7D低表达的患者生存较差(P<0.05);其他microRNA高、低表达者间生存差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表2、图1。
2.3影响卵巢癌生存的因素以年龄(岁:<59=0,59=1)、肿瘤分级(G1+G2=0,G3+G4=1)、病发位置(单侧=0,双侧=1)、临床分期(Ⅰ期+Ⅱ期=0,Ⅲ期+Ⅳ期=1,未知=3)、肿瘤残余(<10 mm=0, 10 mm= 1)、Let-7D(低表达=0,高表达=1)为自变量,以生存结局(生存=0,死亡=1)为因变量,Cox回归分析显示,Let-7D低表达是卵巢癌患者生存的独立危险因素,见表3。
3 讨论
microRNA是一种非编码的核酸分子,可以与其靶基因的3′UTR结合,降解或者抑制mRNA的翻译,进而降低靶基因的表达[10]。研究显示,miR-155在乳腺癌和非小细胞肺癌中具有促进肿瘤进展的作用,在三阴乳腺癌和肺癌中高表达miR-155可以抑制细胞凋亡促进细胞生长,证实了miR-155可作为癌基因参与到肿瘤的进展过程中[11- 12]。本研究结果显示,癌旁组miR-155表达水平低于卵巢癌组,提示miR-155可能具有促进细胞增殖的作用,癌组织中细胞的增殖能力强于癌旁组织,与上述研究一致。另有研究认为,miR-101-1可以作为癌症患者预后的标志物,但是在癌症中的生物学功能尚不明确[13-14]。miR-770可以通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路下游分子F-box和WD重复结构域包含7(F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7,FBXW7)来促进肝癌细胞的增殖、侵袭与迁移[15]。众所周知,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路是广泛存在的一条信号通路,对多种癌症的发生起重要作用。本研究结果显示,癌旁组miR-101-1表达水平高于卵巢癌组,而miR-770低于卵巢癌组,提示miR-770可能是癌基因。然而,生存分析显示,3个指标的高、低表达者间生存差异并无统计学意义,考虑原因可能为miR-770和miR-101-1与卵巢癌细胞的迁移能力关系不大,更多的是对卵巢癌细胞的增殖能力有影响,从而导致对预后没有明显影响。
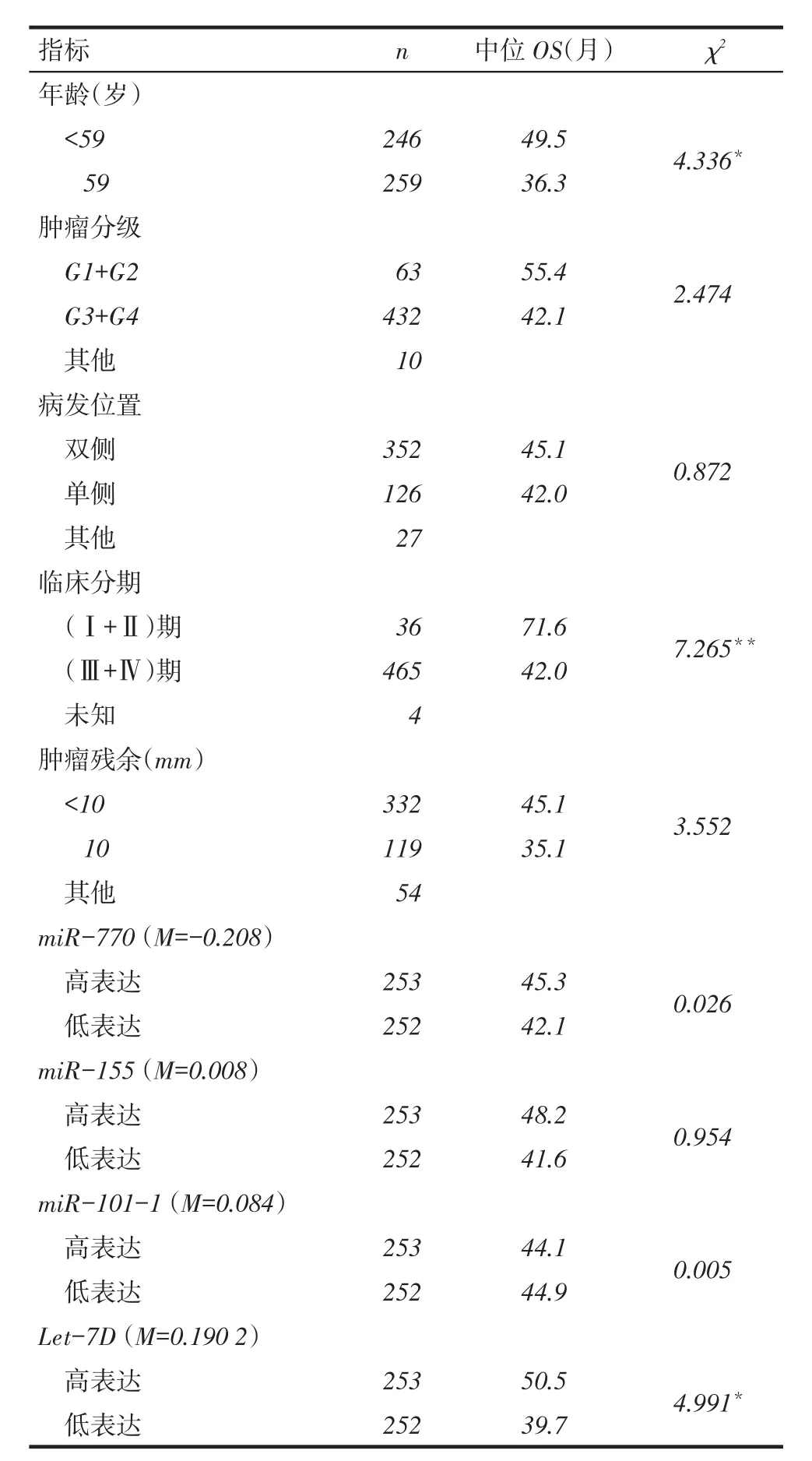
Tab. 2 Univariate analysis of overall survival data in 505 ovary cancer patients表2 505例卵巢癌患者生存分析
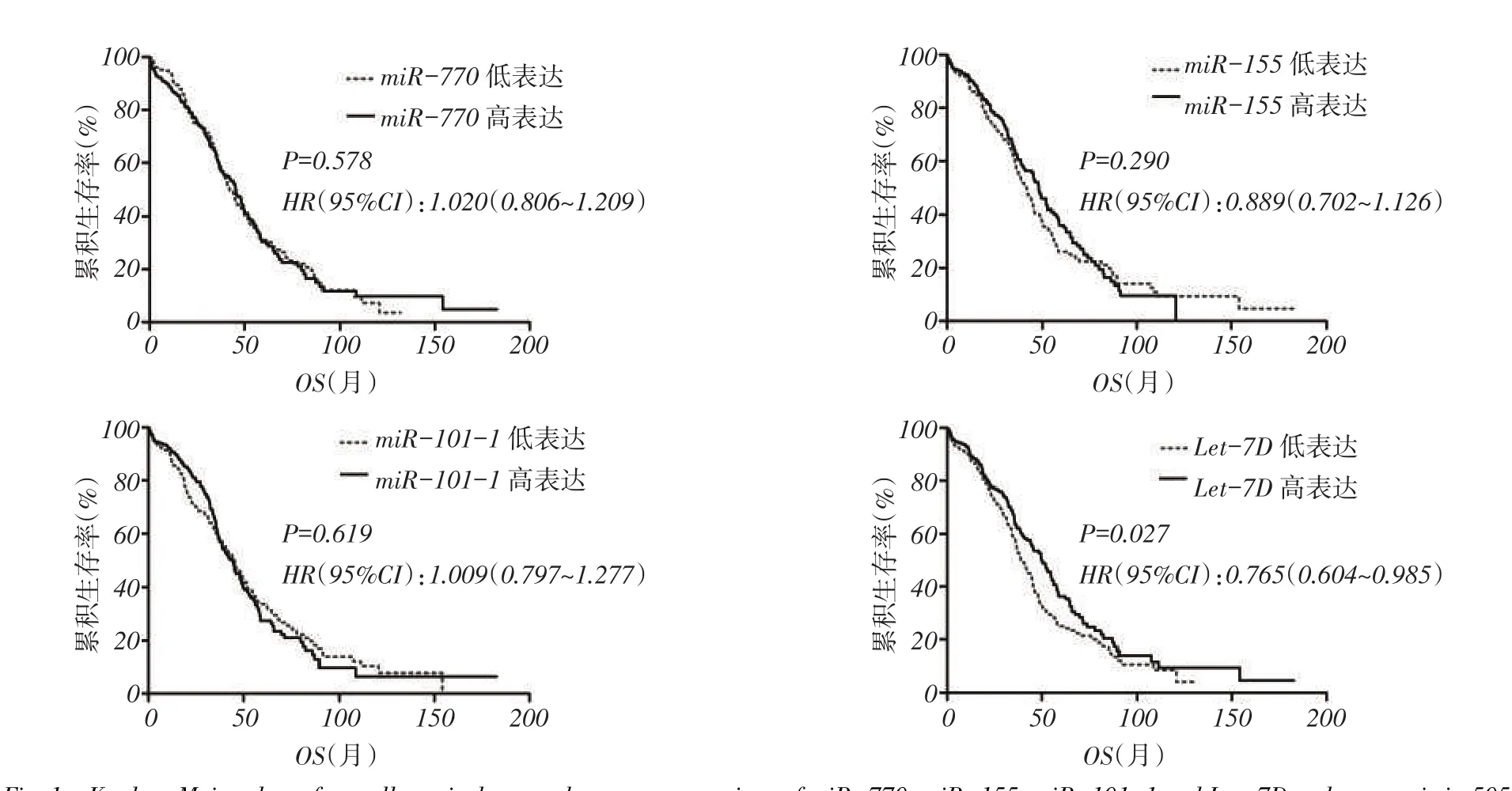
Fig. 1 Kaplan-Meier plots of overall survival curves between expressions of miR-770,miR-155,miR-101-1 and Let-7D and prognosis in 505patients with ovary cancer(Kaplan-Meier,method)图1 505例卵巢癌患者miR-770、miR-155、miR-101-1及Let-7D的表达与预后关系的生存曲线(Kaplan-Meier方法)
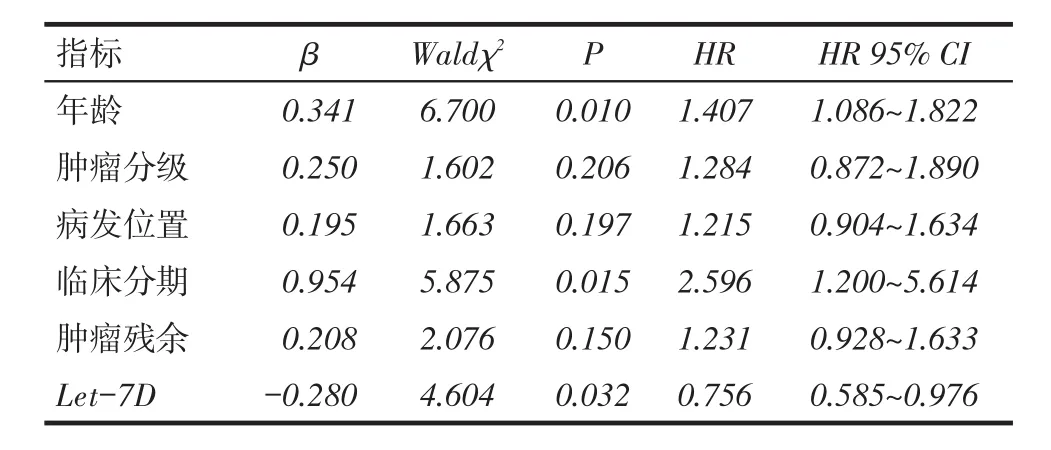
Tab. 3 Cox proportional hazards analysis of survival influencing factors for patients with ovary cancer表3 卵巢癌患者的Cox生存影响因素结果
Let-7家族参与多种肿瘤的发生进展,起到了肿瘤抑制基因的作用。本课题组前期研究发现,卵巢癌患者血浆中高表达Let-7家族的Let-7F-1往往预示预后较差[3]。研究显示,在口腔癌细胞系中敲低Let-7D的表达可以提高Twist和Snail的表达,进而增强口腔癌细胞系的侵袭迁移能力,促进上皮间质转换[16]。另有研究证实,在卵巢癌细胞系中胰岛素样生长因子2 mRNA结合蛋白1(insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1,IGF2BP1)和三磷酸腺苷(ATP)结合亚家族B1(ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1,ABCB1)的表达与卵巢癌细胞系对化疗药物的抗性相关,Let-7D可以靶向作用于IGF2BP1,从而降低ABCB1的表达,提高细胞对化疗药物的敏感性[17]。本研究结果显示,Let-7D在卵巢癌患者的癌旁组织中的表达明显高于癌组织,且Let-7D高表达者预后较好,Let-7D低表达是卵巢癌患者生存的独立危险因素,考虑原因可能是高表达Let-7D抑制了IGF2BP1的表达,进而降低了ABCB1的表达,提高了肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的敏感性,最终化疗效果相对较好,进而使卵巢癌患者的寿命得到延长。另有研究显示,Let-7D的功能与免疫系统相关,高表达Let-7D可增强机体免疫力,抵御多种疾病[18]。
综上所述,miR-155、miR-770在癌组织中的表达水平高于癌旁组织,可能具有促进卵巢癌细胞增殖的功能;miR-101-1和Let-7D的表达水平癌旁高于癌组织,且Let-7D与预后相关,是卵巢癌患者预后的独立影响因素,很有希望成为卵巢癌患者预后的临床指标。然而有研究显示,miR-200a的表达与卵巢癌患者预后有关,可能也是卵巢癌患者预后预测的独立影响因素[19]。因此,多种microRNA有可能成为卵巢癌患者预后的预测指标,而对相关microRNA进行综合分析可能更有助于提高卵巢癌诊断和预后评判的价值。
[1]DeSantis CE,Lin CC,Mariotto AB,et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics,2014[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2014,64(4):252-271. doi:10.3322/caac.21235.
[2]Siegel R,Naishadham D,Jemal A. Cancer statistics,2012[J]. CA Cancer JClin,2012,62(1):10-29. doi:10.3322/caac.20138.
[3]Zheng H,Liu JY,Song FJ,et al. Advances in circulating microRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic markers for ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Biol Med,2013,10(3):123-130. doi:10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2013.03.001.
[4]Li J,Li D,Zhang W. Tumor suppressor role of miR-217 in human epithelial ovarian cancer by targeting IGF1R[J]. Oncol Rep,2016,35 (3):1671-1679. doi:10.3892/or.2015.4498.
[5]Lee M,Kim EJ,Jeon MJ. MicroRNAs 125a and 125b inhibit ovarian cancer cells through post-transcriptional inactivation of EIF4EBP1[J]. Oncotarget,2015,7(8):8726-8742. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6474.
[6]Fu X,Cui Y,Yang S,et al. MicroRNA-613 inhibited ovarian cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating KRAS[J]. Tumour Biol,2015 Dec 2. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4507-7.[Epub ahead of print][7]Yao L,Wang L,Li F,et al. MiR181c inhibits ovarian cancer metastasis and progression by targeting PRKCD expression[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2015,8(9):15198-15205.
[8]Fan JY,Yang Y,Xie JY,et al. MicroRNA-144 mediates metabolic shift in ovarian cancer cells by directly targeting Glut1[J]. Tumour Biol,2015 Dec 1. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4558-9.[Epub ahead of print]
[9]Bowen NJ,Walker LD,Matyunina LV,et al. Gene expression profiling supports the hypothesis that human ovarian surface epithelia are multipotent and capable of servingas ovarian cancer initiatingcells[J]. BMC Med Genomics,2009,2:71. doi:10.1186/1755-8794-2-71.
[10]Bartel DP. MicroRNAs:target recognition and regulatory functions [J]. Cell,2009,136(2):215-233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002.
[11]Liu M,Zhou K,Huang Y,et al. The candidate oncogene(MCRS1) promotes the growth of human lung cancer cells via the miR-155-Rb1 pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2015,34:121. doi:10.1186/s13046-015-0235-5.
[12]Wang Q,Li C,Zhu Z,et al. miR-155-5p antagonizes the apoptotic effect of bufalin in triple-negative breast cancer cells[J]. Anticancer Drugs,2016,27(1):9-16. doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000296.
[13]Miao L,Wang L,Yuan H,et al. MicroRNA-101 polymorphisms and risk of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population[J]. Tumour Biol,2015 Oct 22. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4249-6.[Epub ahead of print]
[14]Li X,Shi Y,Yin Z,et al. An eight-miRNA signature as a potential biomarker for predicting survival in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Transl Med,2014,12:159. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-159.
[15]Wu WJ,Shi J,Hu G,et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signalinginhibits FBXW7 expression by upregulation of microRNA-770 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol,2015,Nov 24. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4452-5.[Epub ahead of print]
[16]Chang CJ,Hsu GG,Chang CH,et al. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial- mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer[J]. Oncol Rep,2011,26(4):1003-1010. doi:10.3892/or.2011.1360.
[17]Jurkovicova D,Lukackova R,Magyerkova M,et al. microRNA expression profiling as supportive diagnostic and therapy prediction tool in chronic myeloid leukemia[J]. Neoplasma,2015,62(6):949-958. doi:10.4149/neo_2015_115.
[18]Kolenda T,Przybyla W,Teresiak A,et al. The mystery of let-7d -a small RNA with great power[J]. Contemp Oncol(Pozn),2014,18 (5):293-301. doi:10.5114/wo.2014.44467.
[19]Liu JY,Zhao YR,Zhan LN,et al. Expression and clinical significance of four miRNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Tianjin Med J,2015,43(9):996-1000.[刘佳宇,赵妍蕊,张丽娜,等.上皮源性卵巢癌中4种miRNAs的表达及其临床意义[J].天津医药,2015,43(9):996-1000]. doi:10.11958/j.issn.0253-9896.2015.09.0010.
(2015-11-25收稿2016-01-05修回)
(本文编辑陆荣展)
The expression and clinical significance of 12 kinds of microRNAs in ovary cancer
TENG Changcai,ZHENG Hong
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center of Cancer,Tianjin 300060,China Corresponding Author E-mail:zhengh1964@163.com
Objective To analyse the expression and clinical significance of 12 kinds of microRNAs(miR)in patients with ovarian cancer using public gene expression databases. Methods The microRNA expression data were screened in dataset GSE14407 and TCGA database,then 12 kinds of microRNAs were obtained including miR-10B,miR-1244,miR-622,miR-21,miR-503,Let-7D,miR-155,miR-30C,miR-17,miR-101-1,miR-186 and miR-770. The expression data of these 12 kinds of microRNAs were compared and identified to find the differential ones between normal tissue and tumors. Data of 505 ovary cancer patients were divided into two groups by age,tumor grade,clinical stage,disease location,tumor residual and microRNA expression. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox multivariate analysis were used to compare the overall survival of ovary cancer patients between two groups. Results Compared with ovary cancer,the expression levels of Let-7D and miR-101-1 were higher,but the expression levels of miR-155 and miR-770 were decreased,in adjacent tissue of ovary tumor(P<0.05). The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis result showed that lower survival rates were found in patients with age 59 years,clinical stage(Ⅲ+Ⅳ)and lower Let-7D expression(P<0.05). The multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that the decreased expression level of Let-7D was the independent risk factor for the prognosis of ovarian cancer. Conclusion The expression of Let- 7D is correlated with the prognosis of ovarian cancer,which is the independent biomarker to predict prognosis of ovarian cancer.
ovarian neoplasms;factor analysis,statistical;microRNA;prognosis;GEO database;TCGA database;Let-7D
R737.31,R34-33
A
10.11958/20150352
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81470153)
天津医科大学肿瘤医院,肿瘤研究所肿瘤分子流行病与生物统计研究室,国家肿瘤临床研究中心,天津市肿瘤防治重点实验室(邮编300060)
滕长财(1990),男,硕士在读,主要从事肿瘤分子生物学研究
E-mail:zhengh64@163.com