陈 清
(湖北省武汉市医疗救治中心感染科 430000)
论着·临床研究
IL-6和IL-13与EV71型肠道病毒感染手足口病患者发病的相关性
陈 清
(湖北省武汉市医疗救治中心感染科 430000)
目的观察肠道病毒71型(EV71)感染手足口病(HFMD)患者血清白细胞介素 (IL)-6和IL-13水平变化情况及其临床意义,并对血清IL-6和IL-13细胞来源进行初步的探讨。方法采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法测定HFMD患者和健康对照血清中IL-6和IL-13水平,比较不同严重程度的HFMD患者血清中IL-6和IL-13水平,并同时检测HFMD患者治疗后血清IL-6和IL-13水平变化情况。流式细胞术(FCM)分析外周血单个核细胞(PBMC)中单核细胞分泌IL-6和T细胞分泌IL-13的情况。EV71病毒感染健康人单核细胞和T细胞后,FCM检测单核细胞分泌IL-6和T细胞分泌IL-13变化情况。结果EV71感染HFMD患者血清 IL-6和IL-13水平分别为(79.63±29.45)pg/mL和(36.45±15.13)pg/mL,健康对照组血清IL-6和IL-13水平分别为(27.26±7.82)pg/mL和(13.46±3.14)pg/mL,HFMD患者血清IL-6和IL-13水平显着高于健康对照者(P<0.01),同时,随着HFMD患者疾病严重程度增加,血清IL-6和IL-13水平亦逐渐升高(P<0.01)。治疗后HFMD患者血清中IL-6和IL-13水平分别为(48.23±23.14)pg/mL和(23.25±9.63)pg/mL,与治疗前相比显着降低(P<0.01)。HFMD患者外周血单核细胞分泌IL-6水平和T细胞分泌IL-13的水平与健康对照者相比显着升高;EV71病毒处理健康人单核细胞和T细胞后单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力显着升高。结论EV71病毒可能时通过促进单核细胞分泌IL-6和T细胞分泌IL-13,致使血清IL-6和IL-13水平升高,从而参与HFMD的发生和发展。
手足口病;白细胞介素-6;白细胞介素-13;肠道病毒71型
手足口病(hand,foot,and mouth disease,HFMD)是儿童常见传染病(主要发生在5岁以下儿童),典型的特征是口痛、厌食、低热、手、足、口腔等部位出现小疱疹或小溃疡,HFMD于1957首次在新西兰报道[1]。可引起HFMD的病毒包括柯萨奇病毒A16(coxsackievirus A16,CVA16)和肠道病毒71型(enterovirus 71,EV71)[2]。其中CVA16所致的HFMD并发症发生率一般低,结局都较好[3]。而EV71所致的HFMD多出现较为严重的神经系统并发症[4-6]。已知EV71是一种具有高度嗜神经性的正义单链RNA病毒,属于小RNA病毒科,肠道病毒属[7-9],在一般情况下,EV71感染主要是引起儿童HFMD和疱疹性咽峡炎[10]。越来越多的证据表明,促炎和抗炎细胞因子可能在EV71所致HFMD发生中发挥关键的作用。目前关于白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-6和IL-13在EV71所致HFMD发生中的作用还很少有研究报道。据此,本研究收集2013年1~12月在本院住院且确诊为EV71感染的HFMD患者30例,观察HFMD患者血清IL-6和IL-13水平变化情况及其临床意义,并对血清IL-6和IL-13细胞来源进行初步的探讨,结果报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 根据“重症EV71感染疾病的临床治疗专家共识”收集2013年1~12月在本院住院且确诊为EV71感染的HFMD 30例,其中临床Ⅱ期(神经系统受累)10例、Ⅲ期(早期心肺衰竭)10例、Ⅳ期(心肺衰竭)10例。EV71感染HFMD的诊断标准:中国卫生部2010年公布的 “手足口病治疗指南”和“粪便EV71病毒”测试呈阳性[11]。患者入院即抽血获取血清,并在疾病康复时再次抽血获取血清。同时收集同期入院健康体检者血清10例,其中男、女各5例,年龄(26.25±11.83)岁。其中Ⅱ、Ⅲ期和Ⅳ期患者男女比例及年龄差异均无统计学意义,具有可比性,详情见表1。

表1 3组HFMD患者临床特征比较
1.2 酶联免疫吸附试验(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)法检测IL-6、IL-16 IL-6和IL-13试剂盒均购自R&D公司,严格按照说明书要求操作如下:将血清样品和标准品100 μL加入孔中,另留出空白对照孔,用封板膜封住反应孔,37 ℃孵育90 min;每孔加入250 μL洗涤液,震荡1 min/次洗板,共4次;加入配制好的生物素化抗体工作液100 μL孔,37 ℃孵育60 min;洗板4次;加入酶结合物工作液100 μL孔,37 ℃孵育30 min;洗板4次;加入显色剂100 μL/well,避光,37 ℃孵育10~20 min;加入终止液100 μL/well,短暂震荡混匀后立即测量OD450值。
1.3 外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cell,PBMC)获取 无菌采集的抗凝血按1∶1的比例缓缓加入已预加淋巴细胞分离液的15 mL离心管中,800×g离心15 min;滴管吸取白膜层,加入装有10 mL无血清RPMI 1640培养基的15 mL离心管中,600×g离心10 min;细胞沉淀以10 mL无血清RPMI 1640培养基重悬,400×g离心8 min;再用1 mL RPMI-1640完全培养基(10 % FBS,200 IU/mL rhIL-2)将细胞沉淀重悬,台盼蓝染色计数后制备成浓度为2×106个/mL的细胞悬液。
1.4 IL-6和IL-13检测方法 无菌分选获取的外周血单个核细胞置于24孔板中,于24孔板中加入100 ng/mL PMA和1 μg/mL离子霉素(Ionomycin)刺激1 h,随后加入高尔基体阻断剂继续孵育5 h;收集细胞,先进性细胞表面分子CD14和CD3染色,后加入0.5 mL细胞膜固定透化液重悬细胞,室温避光30 min;以透化液洗涤细胞2次后加入相应荧光抗体(IL-6和IL-13),室温避光30 min;以透化液洗涤细胞2次,细胞重悬于0.2 mL 1%多聚甲醛固定液中待流式细胞仪检测。
1.5 EV71感染单核细胞和T细胞方法 病毒培养与效价测定方法参见文献报道[12],EV71病毒以感染的病毒数目与细胞数目的比值(multiplicity of infection,MOI)=5的条件感染1×107的PBMC细胞。
1.6 统计学处理 采用SPSS16.0 软件进行统计分析,以t检验或ANOVA检验的方法对数据进行统计分析。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 血清IL-6和IL-13水平分析 如图1所示,EV71感染手足口病患者血清IL-6和IL-13水平显着高于健康对照组(P<0.01),且随着疾病严重程度增加,血清IL-6和IL-13水平亦逐渐升高(P<0.01)。

A:血清IL-6水平检测及其与临床分期相关性;B:血清IL-13水平检测及其与临床分期相关性。
图1 ELISA法检测血清IL-6和IL-13水平及其与临床分期相关性分析
2.2 治疗后患者血清IL-6和IL-13水平检测 如图2所示,治疗后患者血清IL-6和IL-13水平分别为(48.23±23.14)pg/mL和(23.25±9.63)pg/mL,与治疗前的(79.63±29.45)pg/mL和(36.45±15.13)pg/mL相比显着降低(P<0.01)。
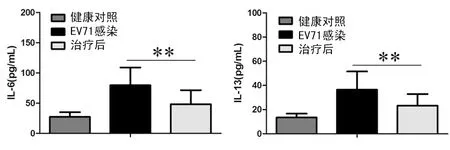
图2 ELISA法检测治疗后患者血清IL-6和IL-13水平
2.3 单核细胞分泌IL-6和T细胞分泌IL-13能力检测 HFMD外周血单核细胞分泌IL-6水平和T细胞分泌IL-13的水平与健康对照者相比显着升高。
2.4 EV71病毒可诱导IL-6和IL-13分泌 EV71病毒处理健康人单核细胞和T细胞后单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力显着升高。
3 讨 论
IL-6是一种重要的促炎性细胞因子,当机体受到病原体感染或出现炎症时,IL-6表达水平会出现显着的升高。同时以往的研究表明,EV71感染的小鼠会出现短暂的IL-6、IL-10和IFN-γ水平升高[13]。EV71感染可大大增加IL-6的释放,IL-6抗体治疗后,小鼠表现为组织损伤程度、病毒载量和B细胞活化水平降低[14]。提示,IL-6在EV71感染HFMD发病过程中具有一定的作用。本研究结果显示,HFMD患者血清IL-6水平显着高于健康对照者,同时,随着HFMD患者疾病严重程度增加,血清IL-6水平亦逐渐升高。该结果与Zhang等[15]通过比较99例EV71感染HFMD患者和19例健康人血清IL-6水平,发现的EV71感染HFMD患者血清IL-6水平显着升高结果相一致。IL-13是一种由T细胞分泌的细胞因子,具有潜在的抗炎活性和抑制单核细胞和巨噬细胞细胞毒活性的作用[16-17]。研究显示,EV71感染引起的肺水肿患者具有较高水平的IL-13分泌[18]。本研究结果显示,HFMD患者血清IL-13水平显着高于健康对照者,同时,随着HFMD患者疾病严重程度增加,血清IL-13水平亦逐渐升高。提示,IL-13在EV71感染HFMD发病过程中具有一定的作用。据此,本研究的上述结果提示,IL-6和IL-13均在EV71感染HFMD发病过程中具有一定的作用。
文献报道,血清中IL-6主要由单核细胞分泌,而IL-13主要由淋巴细胞分泌,据此,作者检测了手足口病患者和健康人外周血单核细胞分泌IL-6和T细胞分泌IL-13的情况,结果发现,手足口病患者外周血单核细胞分泌IL-6水平和T细胞分泌IL-13的水平与健康对照相比显着升高(P<0.01)。提示,手足口病患者血清中异常升高的IL-6和IL-13水平可能是因为单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力升高所致。为了解释单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力升高是否为EV71病毒感染所致,本研究采用EV71病毒处理健康人单核细胞和T细胞,结果发现,EV71病毒可导致健康人单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力升高。据此,上述结果提示,EV71病毒感染可通过上调单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13的能力,进而导致手足口病的发生。文献报道,EV71感染后T淋巴细胞瘤Jurkat细胞分泌子IL-2、IFN-α、IL-6和IL-10的能力下降[12],这一结果与本研究结果存在矛盾之处。推测可能的原因是本研究采用的是新鲜分离的单核细胞和T细胞,而文献中采用的是淋巴瘤细胞,而瘤变的细胞功能本身就会出现异常的改变,同时实验环境的不同也会导致不同结果的出现,据此可能使得本研究结果与文献报道不同。
综述所述,本研究结果初步提示EV71病毒可能时通过促进单核细胞分泌IL-6和T细胞分泌IL-13,致使血清IL-6和IL-13水平升高,从而参与HFMD的发生和发展。研究显示,EV71感染后所引发的机体免疫功能紊乱、细胞炎症因子异常级联活化等一系列改变均与Toll样受体(toll like receptor,TLR)密切相关[19-21]。然而,在手足口病患者中,EV71病毒感染所致单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力升高是否与TLR相关,以及EV71病毒感染所致单核细胞和T细胞分泌IL-6和IL-13能力升高的机制还有待进一步的深入研究。
[1]Robinson CR,Doane FW,Rhodes AJ.Report of an outbreak of febrile illness with pharyngeal lesions and exanthem:Toronto,summer 1957;isolation of group A Coxsackie virus[J].Can Med Assoc J,1958,79(3):615-621.
[2]Zhu Z,Zhu S,Guo X,et al.Retrospective seroepidemiology indicated that human enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 circulated wildly in central and southern China before large-scale outbreaks from 2008[J].Virol J,2010,7(1):300.
[3]Chang LY,Lin TY,Huang YC,et al.Comparison of enterovirus 71 and coxsackie-virus A16 clinical illnesses during the Taiwan enterovirus epidemic,1998[J].Pediatr Infect Dis J,1999,18(12):1092-1096.
[4]Chen F,Li JJ,Liu T,et al.Clinical and neuroimaging features of enterovirus71 related acute flaccid paralysis in patients with hand-foot-mouth disease[J].Asian Pac J Trop Med,2013,6(1):68-72.
[5]Chua KB,Kasri AR.Hand Foot and Mouth Disease Due to Enterovirus 71 in Malaysia[J].Virol Sin,2011,26(4):221-228.
[6]Ooi MH,Wong SC,Lewthwaite P,et al.Clinical features,diagnosis and management of human enterovirus 71 infection[J].Lancet Neurol,2010,9(11):1097-1105.
[7]Lu J,He YQ,Yi LN,et al.Viral kinetics of Enterovirus 71 in human habdomyosarcoma cells[J].World J Gastroenterol,2011,17(36):4135-4142.
[8]Yi L,He Y,Chen Y,et al.Potent inhibition of human enterovirus 71 replication by type I interferon sub-types[J].Antiviral Therapy,2011,16(1):51-58.
[9]Liao CC,Liou AT,Chang YS,et al.Immunodeficient mouse models with different disease profiles by in vivo infection with the same clinical isolate of enterovirus71 [J].J Virol,2014,88(21):12485-12499.
[10]Huang SW,Lee YP,Hung YT,et al.Exogenous interleukin-6,interleukin-13,and interferon-gamma provoke pulmonary abnormality with mild edema in enterovirus 71-infected mice[J].Respir Res,2011(12):147.
[11]蔡榕,郭岚峰.EV71所致重症手足口病患儿的临床分析及其预防控制措施[J].现代预防医学,2011,38(22):4618-4619.
[12]杜伯雨,白璐,沈岩,等.肠道病毒EV71感染对T细胞免疫功能影响研究[J].医学研究杂志,2010,39(8):50-53.
[13]Huang SW,Lee YP,Hung YT,et al.Exogenous interleukin-6,interleukin-13,and interferon-γ provoke pulmonary abnormality with mild edema in enterovirus 71-infected mice[J].Respir Res,2011,6(12):147.
[14]Khong WX,Foo DG,Trasti SL,et al.Sustained high levels of interleukin-6 contribute to the pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 in a neonate mouse model[J].J Virol,2011,85(7):3067-3076.
[15]Zhang Y,Liu H,Wang L,et al.Comparative study of the cytokine/chemokine response in children with differing disease severity in enterovirus 71-induced hand,foot,and mouth disease[J].PLoS One,2013,8:e67430.
[16]Minty A,Chalon P,Derocq JM,et al.Interleukin-13 is a new human lymphokine regulating inflammatory and immune responses[J].Nature,1993,362(6417):248-250.
[17]De Vries JE.The role of IL-13 and its receptor in allergy and inflammatory responses[J].J Allergy Clin Immunol,1998,102(5):165-169.
[18]Chen ZF,Li RQ,Xie ZC,et al.IL-6,IL-10 and IL-13 are associated with pathogenesis in children with Enterovirus 71 infection[J].Int J Clin Exp Med,2014,7(9):2718-2723.
[19]马慧敏,欧维琳.Toll样受体在EV71感染发病机制中的作用[J].华夏医学,2014,27(4):132-135.
[20]景志忠,何小兵,房永祥,等.病毒感染对宿主TLRs模式识别与免疫应答信号的影响[J].病毒学报,2012,28(4):453-461.
[21]Triantafilou K,Vakakis E,Richer EA,et al.Human rhinovirus recognition in non-immune cells is mediated by Toll-like receptors and MDA-5,which trigger a synergetic proinflammatory immune response[J].Virulence,2011,2(1):22-29.
Enterovirus 71 infection induced HFMD related to IL-6 and IL-13 level
ChenQing
(InfectionsDepartment,WuhanMedicalTreatmentCenter,Hubei430000,China)
ObjectiveTo study the clinical significance of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-13 levels in serum of hand,foot,and mouth disease (HFMD) caused by enterovirus 71,and carries on the preliminary discussion on serum IL-6 and IL-13 cell origin.MethodsSerum levels of IL-6 and IL-13 in HFMD and healthy control were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA),serum IL-6 and IL-13 levels among different severity of HFMD were compared.Serum IL-6 and IL-13 levels in HFMD after treatment were also detected.The secretion of IL-6 by monocyte and the secretion of IL-13 by T cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were detected by Flow Cytometry (FCM).Monocyte and T cells from health individual were treated with EV71,and the secretion of IL-6 by monocyte and the secretion of IL-13 by T cells were detected by FCM too.ResultsSerum levels of IL-6 and IL-13 were (79.63±29.45) pg/mL and (36.45±15.13) pg/mL respectively in HFMD,and serum levels of IL-6 and IL-13 were (27.26±7.82) pg/mL and (13.46±3.14) pg/mL respectively in health control,serum IL-6 and IL-13 levels in HFMD were significantly higher than that of healthy subjects (P<0.01),and the mean serum IL-6 and IL-13 levels of HFMD were increased with the severity of the disease (P<0.01).After treatment,serum levels of IL-6 and IL-13 were (48.23±23.14) pg/mL and (23.25±9.63) pg/mL respectively,when compared with before treatment,serum levels of IL-6 and IL-13 were significantly decreased (P<0.01).The secretion ability of IL-6 by monocyte and the secretion of IL-13 by T cells in HFMD were significantly higher than that of healthy subjects.After infection by EV71,the secretion ability of IL-6 by monocyte and the secretion of IL-13 by T cells were significantly increased.ConclusionInfection of EV71 probably by increase the secretion ability of IL-6 by monocyte and the secretion of IL-13 by T cells,resulted in elevated of serum IL-6 and IL-13 levels,which involved in the occurrence and development of HFMD.
hand,foot and mouth disease;interleukin-6;interleukin-13;enterovirus 71
10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2015.26.011
陈清(1969-),本科,副主任医师,主要从事感染疾病方面的研究。
R725.1
A
1671-8348(2015)26-3634-03
2015-04-08
2015-06-15)