刘毅+由凤鸣+严然+张晓丹
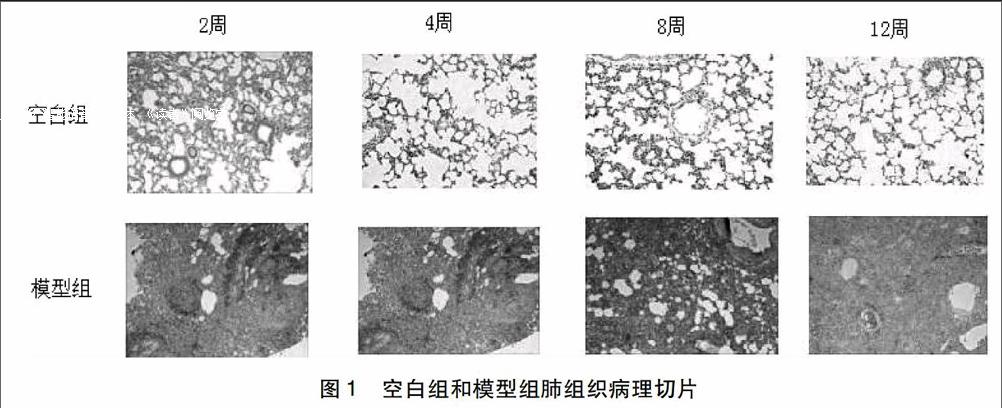
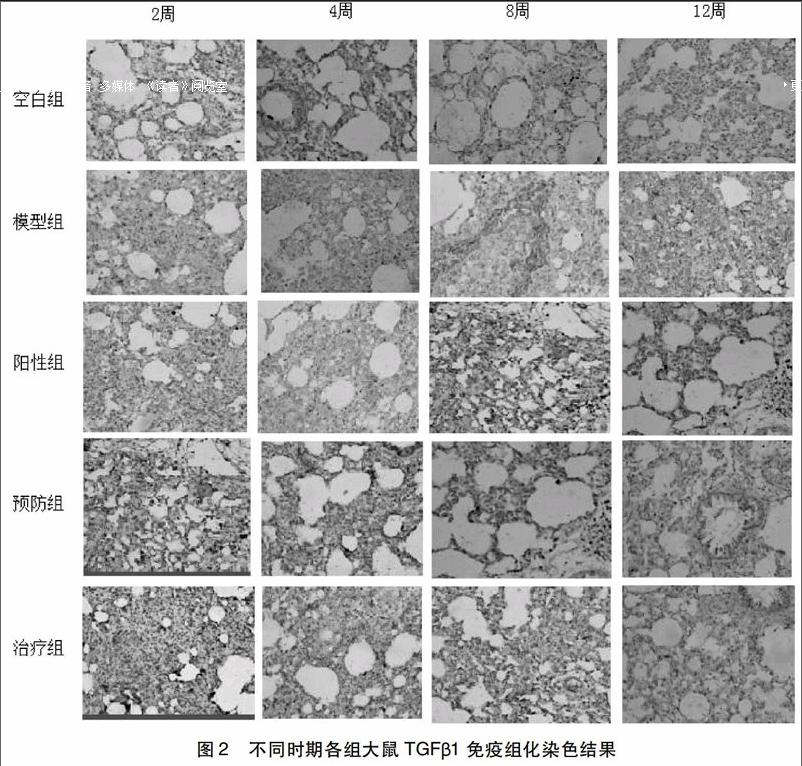
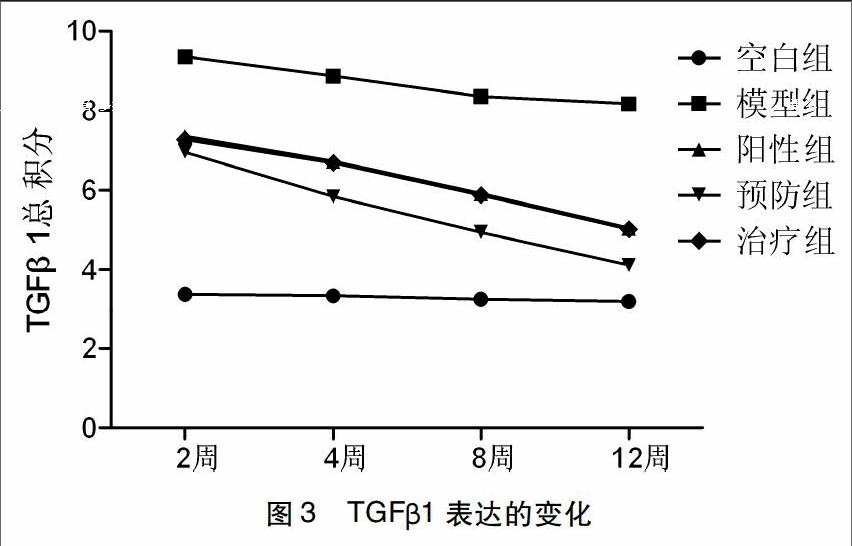
摘要:目的观察桑杏清营汤对放射性肺炎大鼠肺组织中TGF-β1表达的影响,探讨成都中医药大学附属医院防治放射性肺炎的经验方桑杏清营汤对大鼠放射性肺炎(Radiation Pneumonitis,RP)的疗效及作用机制。方法将180只8周龄、体重约为280 g~300 g的SPF级雄性SD大鼠,随机分为空白对照组(空白组),照射模型组(模型组),西药治疗组(阳性组),中药预防组(预防组),中药治疗组(治疗组),每组36只。除外空白组均给予直线加速器6MV-X线,20 gy照射1次。除预防组于照射前4天开始灌服桑杏清营汤外,其余各组造模后第二天开始,空白组、模型组给予等容积的生理盐水灌胃,治疗组灌服桑杏清营汤,阳性组给予醋酸泼尼松混悬液,每日1次,5d/周。照射后第2、4、8、12周每组随机取9只。将右肺组织固定于福尔马林溶液中,石蜡包埋,切片,HE染色光镜下观察肺组织病理形态学变化,免疫组化法检测TGFβ1表达。结果光镜下模型对照组较正常组肺组织炎症细胞浸润、结构破坏明显,模型组与空白组大鼠比较肺组织TGF-β1的表达显着升高(P<0.01),提示造模成功;与桑杏清营汤相比,模型组肺组织TGF-β1的表达升高(P<0.05),其中桑杏清营汤预防组(P<0.01);结论桑杏清营汤防治放射性肺炎可能是通过抑制TGF-β1/Smad信号转导通路,从而抑制大鼠肺组织中TGF-β1的表达,延缓并减轻肺纤维化。
关键词:放射性肺炎;桑杏清营汤;肺组织;TGFβ1;TGF-β1/Smad通路
中图分类号:R285.5文献标志码:A文章编号:1007-2349(2017)04-0078-04
Study on the Effect of Sangxingqingying Decoction on Expression
of TGF-β1 in Radiation Pneumonia Tissue
LIU Yi1,3, YOU Feng-ming1, YAN Ran1, ZHANG Xiao-dan2
(1. Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan;
2. Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, Sichuan;
3. Sichuan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan)
【Abstract】Objective: To observe the effect of Sangxingqingying Decoction on the expression of TGF-β1 in radiation pneumonia tissue of rats and to explore its curative effect and mechanism of treating radiation pneumonitis (RP) in the Affiliated Hospital to Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Methods: 180 male SD rats at the age of 8-week old and weighing about 280 g to 300g were randomly divided into a blank control group (blank group), irradiated model group (model group), western medicine treatment group (positive group ), Chinese medicine prevention group (prevention group) and traditional Chinese medicine treatment group (treatment group), 36 rats each group. Except the blank group, all other groups were given linear accelerator 6MV-X line, 20 gy irradiation 1 time. Except the prevention group that was administrated with Sangxingqingying Decoction 4 days before radiation, the rest groups were given Sangxingqingying Decoction in the next day after modeling. The blank group and the model group were given the same volume of saline. The treatment group was given with Sangxingqingying Decoction and the positive group was given prednisone acetate suspension, once a day, 5 days a week. At the 2nd, 4th, 8th and 12th week after irradiation, 9 rats were randomly taken from each group. The right lung tissue was fixed in formalin solution, paraffin embedded and sliced. HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of lung tissue, and immunohistochemical method was used to detect TGFβ1 expression. Results: Compared with the control group, the structural damage of the model group was obvious in the lung tissue inflammation cells infiltration under light microscope. Compared with the control group, the expression of TGF-β1 in lung tissue of the model group and the blank group significantly increased (P<0.01), suggesting that the model was successful. Compared with SangXiangxingqingying Decoction group, the expression of TGF-β1 in lung tissue of the model group increased(P<0.05), including the prevention group(P<0.01). Conclusion: The prevention and treatment of radiation pneumonia with Sangxingqingying Decoction may inhibit the expression of TGF-β1 in the rat lung tissue through the inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signal transduction pathway, and delay and reduce pulmonary fibrosis.