李幼奇 刘珍珍 石咏军 刘冠贤
【摘要】 目的:探讨广东省惠州市成年体检人群慢性肾脏病(CKD)的患病率及相关危险因素。
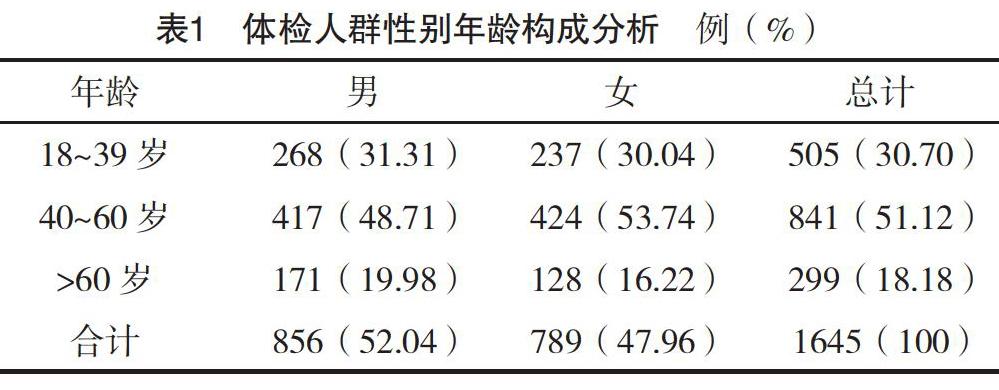
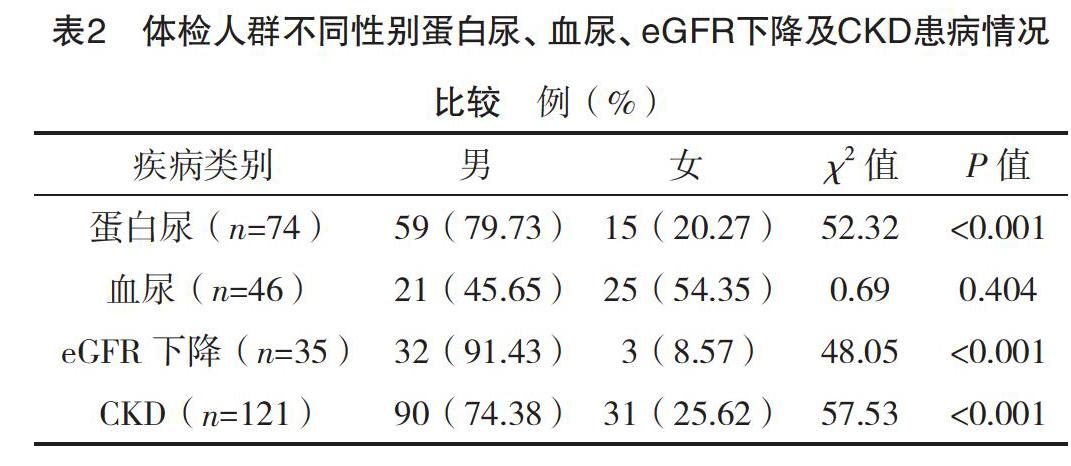
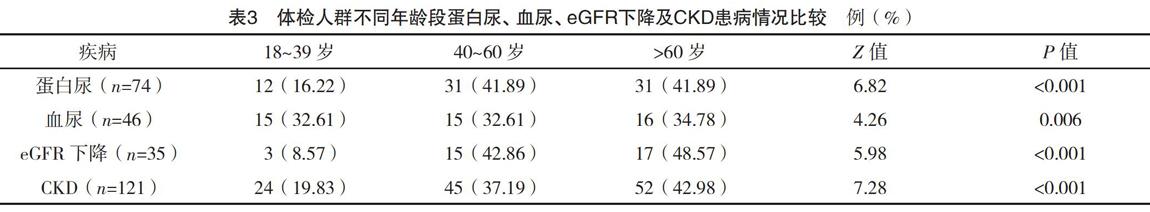
方法:选取2015年4-8月本院进行体检的成年人1 645例,通知尿检结果异常及血肌酐升高者3个月后复查,分析CKD患病情况及相关影响因素。结果:本研究中CKD、蛋白尿、血尿、eGFR下降发生率分别为7.36%、4.50%、2.80%、2.13%,CKD 1~5期占比分别为42.15%、28.10%、23.97%、1.65%、4.13%;男性蛋白尿、eGFR下降及CKD患病率均高于女性(P<0.05),不同年龄受试者蛋白尿、血尿、eGFR下降、CKD患病率比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);CKD组男性比例、>60岁者比例、高血压发生率均高于非CKD组(P<0.05);二分类Logistic回归分析显示,男性、年龄、高血压为CKD患病的危险因素(P<0.05)。结论:惠州市成年体检人群CKD的患病率为7.36%,男性、年龄、高血压为CKD患病的危险因素。
【关键词】 慢性肾脏病; 流行病学; 患病率; 危险因素
Prevalence and Related Risk Factors of Chronic Kidney Disease in Health Checkup Population in Huizhou City/LI Youqi,LIU Zhenzhen,SHI Yongjun,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2019,16(22):0-079
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the prevalence and risk factors of chronic kidney disease(CKD)in adult population who receiving body check in Huizhou city.Method:A total of 1645 adults who underwent physical examination in our hospital from April to August 2015 were selected.The patients with abnormal urine test results and elevated serum creatinine were notified for reexamination 3 months later.The prevalence of CKD and its related factors were analyzed.Result:The incidence of CKD,proteinuria,hematuria and eGFR decreased by 7.36%,4.50%,2.80% and 2.13% respectively.The percentage of CKD in the first to fifth stages was 42.15%,28.10%,23.97%,1.65% and 4.13%,respectively.The prevalence of proteinuria,eGFR decreased and CKD in males was higher than those of females(P<0.05).The prevalence of proteinuria,hematuria,decreased eGFR and CKD in subjects of different ages were compared,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Male,the proportion of people over 60 years old and the incidence of hypertension in CKD group were higher than those of non-CKD group(P<0.05).Logistic analysis showed that male,age and hypertension were risk factors for CKD(P<0.05).Conclusion:The prevalence of CKD was 7.36% among adults in Huizhou,male,age and hypertension were risk factors for CKD.
【Key words】 Chronic kidney disease; Epidemiology; Prevalence rate; Risk factors
First-authors address:Huizhou Municipal Central Hospital,Huizhou 516001,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.22.020
慢性肾脏病(chronic kidney disease,CKD)日渐成为突出的公共健康疾病,据推算,我国每年为终末期肾病患者透析治疗支付约2400亿人民币[1],慢性肾脏疾病的治疗已成为我国及世界公共卫生系统的巨大负担,延缓CKD进展为终末期肾病,早期防治意义重大。CKD的流行病学调查利于增强人们对CKD流行特点的认识,利于疾病的早期防治。国内外开展大规模CKD的流行病学调查已有10年余,早在2007年广州就开展了广州市普通人群CKD的流行病学调查[2],而惠州市目前尚无相关调查研究。本研究以惠州市中心人民医院成年体检人群为调查对象,了解惠州市体检人群中CKD的流行病学特点,为惠州市CKD的防治提供指导,现报道如下。